Emerging Molecular-Genetic Families in Dystonia: Endosome-Autophagosome-Lysosome and Integrated Stress Response Pathways
- PMID: 39467044
- PMCID: PMC11752985
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.30037
Emerging Molecular-Genetic Families in Dystonia: Endosome-Autophagosome-Lysosome and Integrated Stress Response Pathways
Abstract
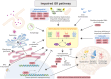
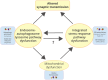
Advances in genetic technologies and disease modeling have greatly accelerated the pace of introducing and validating molecular-genetic contributors to disease. In dystonia, there is a growing convergence across multiple distinct forms of the disease onto core biological processes. Here, we discuss two of these, the endosome-autophagosome-lysosome pathway and the integrated stress response, to highlight recent advances in the field. Using these two pathomechanisms as examples, we further discuss the opportunities that molecular-genetic grouping of dystonias present to transform dystonia care. © 2024 The Author(s). Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: autophagy; endosomal trafficking; dystonia; eIF2 α; Eif2s1; HOPS complex; integrated stress response; ISR; lysosome..
© 2024 The Author(s). Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures

References
-
- Cardoso F, Goetz CG, Mestre TA, et al. A statement of the MDS on biological definition, staging, and classification of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2024;39(2):259–266. - PubMed
-
- Hoglinger GU, Adler CH, Berg D, et al. A biological classification of Parkinson's disease: the SynNeurGe research diagnostic criteria. Lancet Neurol 2024;23(2):191–204. - PubMed
-
- Di Fonzo A, Zech M. Nuclear pore complex dysfunction in dystonia pathogenesis: nucleoporins in the spotlight. Mov Disord 2023;38(1):23–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

