Targeted modulation of pennycress lipid droplet proteins impacts droplet morphology and seed oil content
- PMID: 39467186
- PMCID: PMC11629743
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.17109
Targeted modulation of pennycress lipid droplet proteins impacts droplet morphology and seed oil content
Abstract
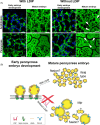
Lipid droplets (LDs) are unusual organelles that have a phospholipid monolayer surface and a hydrophobic matrix. In oilseeds, this matrix is nearly always composed of triacylglycerols (TGs) for efficient storage of carbon and energy. Various proteins play a role in their assembly, stability and turnover, and even though the major structural oleosin proteins in seed LDs have been known for decades, the factors influencing LD formation and dynamics are still being uncovered mostly in the "model oilseed" Arabidopsis. Here we identified several key LD biogenesis proteins in the seeds of pennycress, a potential biofuel crop, that were correlated previously with seed oil content and characterized here for their participation in LD formation in transient expression assays and stable transgenics. One pennycress protein, the lipid droplet associated protein-interacting protein (LDIP), was able to functionally complement the Arabidopsis ldip mutant, emphasizing the close conservation of lipid storage among these two Brassicas. Moreover, loss-of-function ldip mutants in pennycress exhibited increased seed oil content without compromising plant growth, raising the possibility that LDIP or other LD biogenesis factors may be suitable targets for improving yields in oilseed crops more broadly.
Keywords: arabidopsis thaliana; endoplasmic reticulum; lipid droplet proteins; lipid droplets; pennycress; seeds; seipin; thlaspi arvense; triacylglycerols.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Plant Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
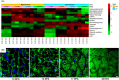
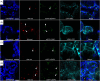

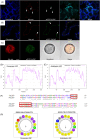
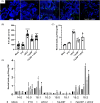



References
-
- Alameldin, H. , Izadi‐Darbandi, A. , Smith, S.A. , Balan, V. , Jones, A.D. , Ebru Orhun, G. et al. (2017) Metabolic engineering to increase the corn seed storage lipid quantity and change its compositional quality. Crop Science, 57, 1854–1864.
-
- Andrews, S. (2010) FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. UK: Babraham Institute.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DE-SC0021286/US Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- DE-SC0020325/US Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- 2019-69012-29851/National Institute of Food and Agriculture, Agriculture and Food Research Initiative, U.S. Department of Agriculture
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

