GULP1 as a Downstream Effector of the Estrogen Receptor-β Modulates Cisplatin Sensitivity in Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 39467629
- PMCID: PMC11534028
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20472
GULP1 as a Downstream Effector of the Estrogen Receptor-β Modulates Cisplatin Sensitivity in Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Background/aim: Precise molecular mechanisms underlying resistance to cisplatin-based chemotherapy remain unclear, while the activity of estrogen receptor-β (ERβ) has been suggested to be associated with chemosensitivity in urothelial cancer. We aimed to determine if GULP1, an adapter protein known to facilitate phagocytosis, could represent a downstream effector of ERβ and thereby modulate cisplatin sensitivity in bladder cancer.
Materials and methods: GULP1 expression and cisplatin cytotoxicity were compared in bladder cancer lines. Immunohistochemistry was used to determine the expression of GULP1 and ERβ in two sets of tissue microarray (TMA) consisting of transurethral resection specimens.
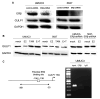
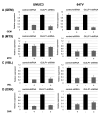
Results: The levels of GULP1 expression were considerably higher in ERβ-knockdown sublines than in the respective control ERβ-positive sublines. Estradiol treatment reduced GULP1 expression in ERα-negative/ERβ-positive lines, which was restored by the anti-estrogen tamoxifen. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay revealed the binding of ERβ to the GULP1 promoter in bladder cancer cells. Moreover, GULP1 knockdown sublines were significantly more resistant to cisplatin treatment, but not to other chemotherapeutic agents, including gemcitabine, methotrexate, vinblastine, and doxorubicin. In the first set of TMA (n=129), the expression of ERβ and GULP1 was inversely correlated (p=0.023), and ERβ(-)/GULP1(+) in 51 muscle-invasive tumors was associated with significantly lower risk of disease progression and cancer-specific mortality. Similarly, in the second set (n=43), patients with ERβ(-)/GULP1(+) muscle-invasive disease were significantly (p=0.021) more likely to be responders to cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy before radical cystectomy.
Conclusion: ERβ activation was found to reduce the expression of GULP1 as a direct downstream target in bladder cancer cells, resulting in the induction of cisplatin resistance.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; GULP1; chemotherapy; cisplatin; estrogen receptor-β.
Copyright © 2024, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest or financial ties related to this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Androgen Receptor Signaling Induces Cisplatin Resistance via Down-Regulating GULP1 Expression in Bladder Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 17;22(18):10030. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810030. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576193 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor-β signaling induces cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Aug 1;10(8):2523-2534. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32905529 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of estrogen receptors-alpha and -beta in bladder cancer cell lines and human bladder tumor tissue.Cancer. 2006 Jun 15;106(12):2610-6. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21945. Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16700038
-
The Nrf2 transcription factor contributes to resistance to cisplatin in bladder cancer.Urol Oncol. 2014 Aug;32(6):806-14. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 May 16. Urol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24837013
-
Association Between Estrogen Receptors and GATA3 in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Their Clinicopathological Significance.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 8;12:684140. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.684140. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34690921 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in understanding the role of sex hormone receptors in urothelial cancer.Oncol Res. 2025 May 29;33(6):1255-1270. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.062142. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40486871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Bladder Cancer National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, Maryland, USA. Available at: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html. [Last accessed on June 21, 2024]
-
- Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Compérat E, Zigeuner R, Sylvester RJ, Burger M, Cowan NC, Gontero P, Van Rhijn BW, Mostafid AH, Palou J, Shariat SF. European Association of Urology guidelines on upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: 2017 update. Eur Urol. 2018;73(1):111–122. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.07.036. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
