LncRNA BRE-AS1 regulates the JAK2/STAT3-mediated inflammatory activation via the miR-30b-5p/SOC3 axis in THP-1 cells
- PMID: 39468152
- PMCID: PMC11519362
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77265-1
LncRNA BRE-AS1 regulates the JAK2/STAT3-mediated inflammatory activation via the miR-30b-5p/SOC3 axis in THP-1 cells
Abstract
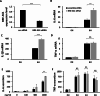
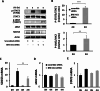
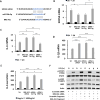
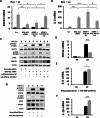
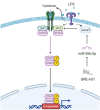
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as pivotal regulators in numerous biological processes, including macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses, which play a critical role in the progress of diverse diseases. This study focuses on the regulatory function of lncRNA brain and reproductive organ-expressed protein (BRE) antisense RNA 1 (BRE-AS1) in modulating the inflammatory activation of monocytes/macrophages. Employing the THP-1 cell line as a model, we demonstrate that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment significantly upregulates BRE-AS1 expression. Notably, specific knockdown of BRE-AS1 via siRNA transfection enhances LPS-induced expression of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1β, while not affecting tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels. This selective augmentation of pro-inflammatory cytokine production coincides with increased phosphorylation of Janus kinase (JAK)2 and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3. Furthermore, BRE-AS1 suppression results in the downregulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)3, an established inhibitor of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Bioinformatics analysis identified binding sites for miR-30b-5p on both BRE-AS1 and SOCS3 mRNA. Intervention with a miR-30b-5p inhibitor and a synthetic RNA fragment that represents the miR-30b-5p binding site on BRE-AS1 attenuates the pro-inflammatory effects of BRE-AS1 knockdown. Conversely, a miR-30b-5p mimic replicated the BRE-AS1 attenuation outcomes. Our findings elucidate the role of lncRNA BRE-AS1 in modulating inflammatory activation in THP-1 cells via the miR-30b-5p/SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, proposing that manipulation of macrophage BRE-AS1 activity may offer a novel therapeutic avenue in diseases characterized by macrophage-driven pathogenesis.
Keywords: JAK2; LncRNA; SOCS3; STAT3; miRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
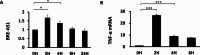
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

