Automatic identification of coronary stent in coronary calcium scoring CT using deep learning
- PMID: 39468230
- PMCID: PMC11519327
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-76092-8
Automatic identification of coronary stent in coronary calcium scoring CT using deep learning
Abstract
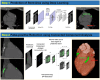
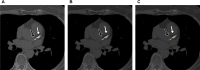
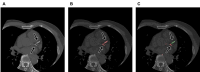
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring CT is a useful tool for screening coronary artery disease and for cardiovascular risk stratification. However, its efficacy in patients with coronary stents, who had pre-existing coronary artery disease, remains uncertain. Historically, CAC CT scans of these patients have been manually excluded from the CAC scoring process, even though most of the CAC scoring process is now fully automated. Therefore, we hypothesized that automating the filtering of patients with coronary stents using artificial intelligence could streamline the entire CAC workflow, eliminating the need for manual intervention. Consequently, we aimed to develop and evaluate a deep learning-based coronary stent filtering algorithm (StentFilter) in CAC scoring CT scans using a multicenter CAC dataset. We developed StentFilter comprising two main processes: stent identification and false-positive reduction. Development utilized 108 non-enhanced echocardiography-gated CAC scans (including 74 with manually labeled stents), and for false positive reduction, 2063 CAC scans with significant coronary calcium (average Agatston score: 523.8) but no stents were utilized. StentFilter's performance was evaluated on two independent internal test sets (Asan cohort- and 2; n = 355 and 396; one without coronary stents) and two external test sets from different institutions (n = 105 and 62), each with manually labeled stents. We calculated the per-patient sensitivity, specificity, and false-positive rate of StentFilter. StentFilter demonstrated a high overall per-patient sensitivity of 98.8% (511/517 cases with stents) and a false-positive rate of 0.022 (20/918). Notably, the false-positive ratio was significantly lower in the dataset containing stents (Asan cohort-1; 0.008 [3/355]) compared with the dataset without stents (Asan cohort-2; 0.043 [17/396], p = 0.008). All false-positive identifications were attributed to dense coronary calcifications, with no false positives identified in extracoronary locations. The automated StentFilter accurately distinguished coronary stents from pre-existing coronary calcifications. This approach holds potential as a filter within a fully automated CAC scoring workflow, streamlining the process efficiently.
Keywords: Accuracy; Artificial intelligence; Computed tomography; Coronary artery calcium score; Coronary stent.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fully Automatic Coronary Calcium Score Software Empowered by Artificial Intelligence Technology: Validation Study Using Three CT Cohorts.Korean J Radiol. 2021 Nov;22(11):1764-1776. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2021.0148. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Korean J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34402248 Free PMC article.
-
Automated coronary artery calcification scoring in non-gated chest CT: agreement and reliability.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 13;9(3):e91239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091239. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24625525 Free PMC article.
-
An evaluation of automatic coronary artery calcium scoring methods with cardiac CT using the orCaScore framework.Med Phys. 2016 May;43(5):2361. doi: 10.1118/1.4945696. Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27147348
-
Meta-analysis of deep learning approaches for automated coronary artery calcium scoring: Performance and clinical utility AI in CAC scoring: A meta-analysis: AI in CAC scoring: A meta-analysis.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Dec;183:109295. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.109295. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39437607
-
The Future of Concurrent Automated Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring on Screening Low-Dose Computed Tomography.Cureus. 2020 Jun 12;12(6):e8574. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8574. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32670710 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Greenland, P. et al. ACCF/AHA 2007 clinical expert consensus document on coronary artery calcium scoring by computed tomography in global cardiovascular risk assessment and in evaluation of patients with chest pain: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Clinical Expert Consensus Task Force (ACCF/AHA Writing Committee to Update the 2000 Expert Consensus Document on Electron Beam Computed Tomography) developed in collaboration with the Society of Atherosclerosis Imaging and Prevention and the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.49, 378–402. 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.10.001 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Blaha, M. J., Mortensen, M. B., Kianoush, S., Tota-Maharaj, R. & Cainzos-Achirica, M. Coronary artery calcium scoring: Is it time for a change in methodology?. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging10, 923–937. 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.05.007 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Hecht, H. S. et al. 2016 SCCT/STR guidelines for coronary artery calcium scoring of noncontrast noncardiac chest CT scans: A report of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography and Society of Thoracic Radiology. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr.11, 74–84. 10.1016/j.jcct.2016.11.003 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

