PcdA promotes orthogonal division plane selection in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 39468247
- PMCID: PMC12323706
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-024-01821-8
PcdA promotes orthogonal division plane selection in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
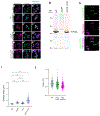
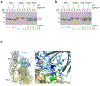
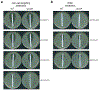
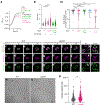
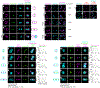
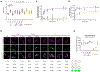
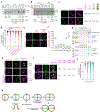
The bacterial pathogen, Staphylococcus aureus, grows by dividing in two alternating orthogonal planes. How these cell division planes are positioned correctly is not known. Here we used chemical genetic screening to identify PcdA as a division plane placement factor. Molecular biology and imaging approaches revealed non-orthogonal division plane selection for pcdA mutant bacteria. PcdA is a structurally and functionally altered member of the McrB AAA+ NTPase family, which are often found as restriction enzyme subunits. PcdA interacts with the tubulin-like divisome component, FtsZ, and the structural protein, DivIVA; it also localizes to future cell division sites. PcdA multimerization, localization and function are NTPase activity-dependent. We propose that the DivIVA/PcdA complex recruits unpolymerized FtsZ to assemble along the proper cell division plane. Although pcdA deletion did not affect S. aureus growth in several laboratory conditions, its clustered growth pattern was disrupted, sensitivity to cell-wall-targeting antibiotics increased and virulence in mice decreased. We propose that the characteristic clustered growth pattern of S. aureus, which emerges from dividing in alternating orthogonal division planes, might protect the bacterium from host defences.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Figures
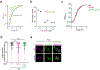




Update of
-
Protein coopted from a phage restriction system dictates orthogonal cell division plane selection in Staphylococcus aureus.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 3:2023.09.03.556088. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.03.556088. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Microbiol. 2024 Nov;9(11):2997-3012. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01821-8. PMID: 37886572 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

