Role of Hippocampal Glutamatergic Synaptic Alterations in Sevoflurane-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction in Aged Mice
- PMID: 39468399
- PMCID: PMC11518816
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70093
Role of Hippocampal Glutamatergic Synaptic Alterations in Sevoflurane-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction in Aged Mice
Abstract
Aims: Perioperative neurocognitive disorders (PND), including postoperative delirium (POD) and postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD), are common following anesthesia and surgery in older patients and significantly increase morbidity and mortality. However, the underlying mechanism of PND is unclear. Our study aims to analyze the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in excitatory neurons and investigate the role of hippocampal glutamatergic synaptic alterations in sevoflurane-induced cognitive dysfunction in aged mice.
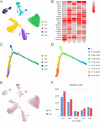
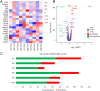
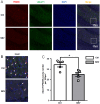
Methods: We performed single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) technology to examine the alterations of excitatory neurons in hippocampus induced by sevoflurane in aged mice. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis of DEGs were performed in excitatory neurons. At last, immunofluorescence staining was used to validate sevoflurane-induced alternation of glutamatergic synapses in the hippocampus of aged mice.
Results: This study demonstrates that DEGs in excitatory neurons are associated with reduction of glutamatergic synapses and cognitive dysfunction. After immunofluorescence staining validation, we also confirmed that sevoflurane anesthesia decreased the density of glutamatergic synapses in the hippocampus of aged mice.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrated a key role of hippocampal glutamatergic synaptic alterations in sevoflurane-induced cognitive dysfunction in aged mice.
Keywords: PND; aging; anesthesia; excitatory neuron; glutamatergic synapse; sevoflurane.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 82371276/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82201321/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 10.13039/100007219/Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai
- JYLJ202308;PI-JiaYan/Clinical Research Program of Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
- 22YF1422500/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

