Magnetic targeting enhances the neuroprotective function of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived iron oxide exosomes by delivering miR-1228-5p
- PMID: 39468528
- PMCID: PMC11514807
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02941-3
Magnetic targeting enhances the neuroprotective function of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived iron oxide exosomes by delivering miR-1228-5p
Abstract
Background: Treating mitochondrial dysfunction is a promising approach for the treatment of post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI). HuMSC-derived exosomes (H-Ex) have shown powerful therapeutic effects in improving mitochondrial function, but the specific effects are unclear and its brain tissue targeting needs to be further optimized.
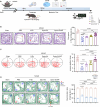
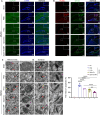
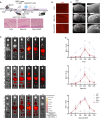
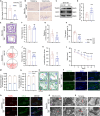
Results: In this study, we found that H-Ex can improve mitochondrial dysfunction of neurons and significantly enhance the cognitive behavior performance of MCAO mice in OGD/R-induced SHSY5Y cells and MCAO mouse models. Based on this, we have developed an exosome delivery system loaded with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Spion-Ex) that can effectively penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The research results showed that under magnetic attraction, Spion-Ex can more effectively target the brain tissue and significantly improve mitochondrial function of neurons after stroke. Meanwhile, we further confirmed that miR-1228-5p is a key factor for H-Ex to improve mitochondrial function and cognitive behavior both in vivo and in vitro. The specific mechanism is that the increase of miR-1228-5p mediated by H-Ex can inhibit the expression of TRAF6 and activate the TRAF6-NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) pathway, thereby exerting protective effects against oxidative damage. More importantly, we found that under magnetic attraction, Spion-Ex exhibited excellent cognitive improvement effects by delivering miR-1228-5p.
Conclusions: Our research found that H-Ex has a good therapeutic effect on PSCI by increasing the expression of miR-1228-5p in PSCI, while H-Ex loaded with Spion-Ex exhibited more excellent effects on improving mitochondrial function and cognitive impairment under magnetic attraction, which can be used as a novel strategy for the treatment of PSCI.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Exosomes; Oxidative stress; Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Mijajlović MD, Pavlović A, Brainin M, Heiss W-D, Quinn TJ, Ihle-Hansen HB, Hermann DM, Assayag EB, Richard E, Thiel A, Kliper E, Shin Y-I, Kim Y-H, Choi S, Jung S, Lee Y-B, Sinanović O, Levine DA, Schlesinger I, Mead G, Milošević V, Leys D, Hagberg G, Ursin MH, Teuschl Y, Prokopenko S, Mozheyko E, Bezdenezhnykh A, Matz K, Aleksić V, Muresanu D. Korczyn AD, Bornstein NM. Post-stroke dementia - a comprehensive review. BMC Med. 2017;15:11. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

