N, N-Dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate-based core/shell microgels loaded with silver nanoparticles for catalysis
- PMID: 39469013
- PMCID: PMC11513783
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra06157h
N, N-Dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate-based core/shell microgels loaded with silver nanoparticles for catalysis
Abstract
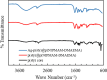
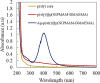
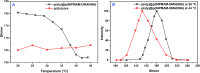
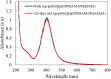
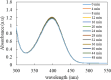
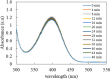
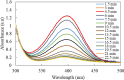
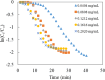
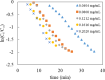
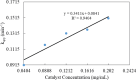
In this work, poly(styrene)@poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide-co-2-(N,N-dimethyl)aminoethyl methacrylate [p(sty)@p(NIPMAM-DMAEMA)] core/shell microgel particles were produced by a two-step free-radical precipitation polymerization process. Ag nanoparticles were successfully embedded inside the sieves of a crosslinked network by using silver nitrate as the precursor salt and NaBH4 as the reductant. The synthesized pure and hybrid microgels were analyzed by various characterization tools, including Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and UV-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopies, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Results indicate the successful fabrication of spherical silver nanoparticles with diameters ranging from 10 to 15 nm within the sieves of the poly(styrene)@poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide-co-2-(N,N-dimethyl)aminoethyl methacrylate) core/shell microgels, which have a hydrodynamic diameter of 155 ± 25 nm. The Ag nanomaterial exhibited long-term stability in the p(sty)@p(NIPMAM-DMAEMA) system due to the strong donor-acceptor relationship between the lone pair of the amide moiety in the polymer microgels and the Ag nanomaterial. The catalytic activity of the Ag-p(sty)@p(NIPMAM-DMAEMA) material was determined by performing the catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol (4-NPh) as a model reaction under diverse concentrations of the catalyst. UV-vis spectrophotometry was used to check the progress of the reaction. The apparent rate constant (k app) was measured by applying the pseudo-first-order kinetics model. It was observed that k app increased with increasing catalyst dose, demonstrating occurrence of the reaction on the surface of the catalyst.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
UV-Vis spectroscopy in the characterization and applications of smart microgels and metal nanoparticle-decorated smart microgels: a critical review.RSC Adv. 2024 Nov 29;14(51):38120-38134. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07643e. eCollection 2024 Nov 25. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39619811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymer hydrogels for stabilization of inorganic nanoparticles and their application in catalysis for degradation of toxic chemicals.Environ Technol. 2023 Apr;44(11):1679-1689. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2021.2011429. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Environ Technol. 2023. PMID: 34821537
-
Fabrication of silver nanoparticles within chitosan based microgels for catalysis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jun 15;240:124401. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124401. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37044327
-
Polymer microgels for the stabilization of gold nanoparticles and their application in the catalytic reduction of nitroarenes in aqueous media.RSC Adv. 2022 Feb 10;12(9):5105-5117. doi: 10.1039/d1ra09380k. eCollection 2022 Feb 10. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35425556 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of UV/Vis Spectroscopy in Characterization and Catalytic Activity of Noble Metal Nanoparticles Fabricated in Responsive Polymer Microgels: A Review.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2018 Nov 2;48(6):503-516. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2018.1451299. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29601210 Review.
Cited by
-
UV-Vis spectroscopy in the characterization and applications of smart microgels and metal nanoparticle-decorated smart microgels: a critical review.RSC Adv. 2024 Nov 29;14(51):38120-38134. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07643e. eCollection 2024 Nov 25. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39619811 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choi B. Lee H. H. Jin S. Chun S. Kim S. H. Nanotechnology. 2007;18:075706. - PubMed
-
- Chen D. Qiao X. Qiu X. Chen J. J. Mater. Sci. 2009;44:1076–1081.
-
- Iyahraja S. Rajadurai J. S. AIP Adv. 2015;5:057103.
-
- Abbasi E. Milani M. Alvi S. F. Kouhi M. Akbarzadeh A. Nasrabdi H. T. Nikasa P. Joo S. W. Hanifehpour Y. koshki K. N. Samiei M. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016;42:173–180. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

