Choroid plexus enlargement in patients with end-stage renal disease: implications for glymphatic system dysfunction
- PMID: 39469069
- PMCID: PMC11513315
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1459356
Choroid plexus enlargement in patients with end-stage renal disease: implications for glymphatic system dysfunction
Abstract
Objectives: The choroid plexus plays a role in eliminating detrimental metabolites from the brain as an integral component of the glymphatic system. This study aimed to investigate alterations in choroid plexus volume in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) compared with healthy controls.
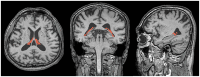
Methods: We enrolled 40 patients with ESRD and 42 healthy controls. They underwent brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), specifically using three dimensional T1-weighted imaging. We analyzed choroid plexus volumes and compared them between patients with ESRD and healthy controls. The diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) index was calculated. We compared the DTI-ALPS index between the ESRD patients and healthy controls. Additionally, we evaluated the association between choroid plexus volume and neuropsychological tests results in patients with ESRD.
Results: There were significant differences in choroid plexus volumes between patients with ESRD and healthy controls. The choroid plexus volumes in patients with ESRD were higher than those in healthy controls (1.392 vs. 1.138%, p < 0.001). The DTI-ALPS index in patients with ESRD was lower than that in healthy controls (1.470 ± 0.239 vs. 1.641 ± 0.266, p = 0.005). There were no differences in choroid plexus volumes between patients with ESRD, regardless of the presence of cognitive impairment. However, among the neuropsychological tests, the scores for word-list recognition in verbal memory were negatively correlated with the choroid plexus volume (r = -0.428, p = 0.006).
Conclusion: We demonstrated a significant enlargement of the choroid plexus volume in patients with ESRD compared to healthy controls. This finding suggests that patients with ESRD have glymphatic system dysfunction, which may be related to cognitive impairment.
Keywords: ESRD; MRI; choroid plexus; cognition; glymphatic system.
Copyright © 2024 Park, Park, Lee, Heo, Ko, Lee and Park.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glymphatic system dysfunction in nondialysis-dependent ESRD patients with diabetic kidney disease: associations with clinical characteristics and cognitive function.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2425160. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2425160. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39506907 Free PMC article.
-
Glymphatic System May Mediate the Relation Between Choroid Plexus and Brain Damage in Multiple Sclerosis.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2025 Jul;12(4):e200414. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200414. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2025. PMID: 40472291 Free PMC article.
-
Choroid Plexus Enlargement in Patients with Chronic Migraine: Implications for Glymphatic System Dysfunction.Can J Neurol Sci. 2025 Feb 10:1-7. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2025.21. Online ahead of print. Can J Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39925124
-
Enlarged choroid plexus in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis may lead to brain structural changes through the glymphatic impairment.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2024 May;85:105550. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2024.105550. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38493535
-
Glymphatic dysfunction mediates the influence of choroid plexus enlargement on information processing speed in patients with white matter hyperintensities.Cereb Cortex. 2024 Jun 4;34(6):bhae265. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae265. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 38912605
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

