Artificial Intelligence in Forensic Sciences: A Systematic Review of Past and Current Applications and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 39469392
- PMCID: PMC11513614
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.70363
Artificial Intelligence in Forensic Sciences: A Systematic Review of Past and Current Applications and Future Perspectives
Abstract
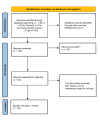
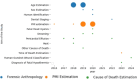
The aim of this study is to review the available knowledge concerning the use of artificial Intelligence (AI) in general in different areas of Forensic Sciences from human identification to postmortem interval estimation and the estimation of different causes of death. This paper aims to emphasize the different uses of AI, especially in Forensic Medicine, and elucidate its technical part. This will be achieved through an explanation of different technologies that have been so far employed and through new ideas that may contribute as a first step to the adoption of new practices and to the development of new technologies. A systematic literature search was performed in accordance with the Preferred Reported Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines in the PubMed Database and Cochrane Central Library. Neither time nor regional constrictions were adopted, and all the included papers were written in English. Terms used were MACHINE AND LEARNING AND FORENSIC AND PATHOLOGY and ARTIFICIAL AND INTELIGENCE AND FORENSIC AND PATHOLOGY. Quality control was performed using the Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tools. A search of 224 articles was performed. Seven more articles were extracted from the references of the initial selection. After excluding all non-relevant articles, the remaining 45 articles were thoroughly reviewed through the whole text. A final number of 33 papers were identified as relevant to the subject, in accordance with the criteria previously established. It must be clear that AI is not meant to replace forensic experts but to assist them in their everyday work life.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; forensic medicine; forensic pathology; forensic sciences; machine learning.
Copyright © 2024, Ketsekioulafis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Madea B. Oxford: Wiley Blackwell; 2014. Handbook of Forensic Medicine.
-
- Overview of artificial intelligence in medicine. Amisha Amisha, Malik P, Pathania M, Rathaur VK. https://journals.lww.com/jfmpc/fulltext/2019/08070/overview_of_artificia.... J Family Med Prim Care. 2019;8:2328–2331. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Learning while searching in constraint-satisfaction-problems. Dechter R. https://cdn.aaai.org/AAAI/1986/AAAI86-029.pdf AAAI 86: Proceedings of the Fifth AAAI National Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 1986:178–183.
-
- Aizenberg I, Aizenberg N, Vanderwalle J. Boston, U.S.A: Springer-Science+Business Media, B.V.; 2000. Multi-Valued and Universal Binary Neurons: Theory, Learning and Applications.
-
- Definition of artificial neural networks with comparison to other networks. Güresen E, Kayakutlu G. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050910004461?via%... Procedia Computer Sci. 2011;3:426–433.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
