Clinical care guidance in patients with diabetes and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A joint consensus
- PMID: 39470335
- PMCID: PMC11524742
- DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000571
Clinical care guidance in patients with diabetes and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A joint consensus
Abstract
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver disease worldwide, affecting >30% of the global population. Metabolic dysregulation, particularly insulin resistance and its subsequent manifestation as type 2 diabetes mellitus, serves as the fundamental pathogenesis of metabolic liver disease. Clinical evidence of the recent nomenclature evolution is accumulating. The interaction and impacts are bidirectional between MASLD and diabetes in terms of disease course, risk, and prognosis. Therefore, there is an urgent need to highlight the multifaceted links between MASLD and diabetes for both hepatologists and diabetologists. The surveillance strategy, risk stratification of management, and current therapeutic achievements of metabolic liver disease remain the major pillars in a clinical care setting. Therefore, the Taiwan Association for the Study of the Liver (TASL), Taiwanese Association of Diabetes Educators, and Diabetes Association of the Republic of China (Taiwan) collaboratively completed the first guidance in patients with diabetes and MASLD, which provides practical recommendations for patient care.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Jee-Fu Huang: consultant of Roche, Gilead, Sysmex, and Aligos. Speaker for Abbvie, BMS, Gilead, Merck, Sysmex, and Roche. Chung-Feng Huang: speaker for Abbvie, BMS, Bayer, Gilead, Merck, and Roche. Chin-Sung Kuo: investigators of clinical trials sponsored by Novo Nordisk and AstraZeneca. Wan-Long Chuang: consultant of Gilead, AbbVie, BMS, PharmaEssentia, and Aligos; Speaker for Gilead, AbbVie, BMS, and PharmaEssentia. Ming-Lung Yu: Research grant from Abbott, BMS, Merck, and Gilead; Consultant of Abbvie, Abbott, Ascletis, BMS, Merck, Gilead, and Roche; Speaker for Abbvie, Abbott, BMS, Merck, Gilead, and IPSEN. The remaining authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures
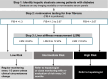



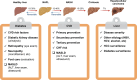
References
-
- Alqahtani SA, Chan WK, Yu ML. Hepatic outcomes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 2023;27:211–23. - PubMed
-
- Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, Anstee QM, Targher G, Romero-Gomez M, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. 2020;73:202–9. - PubMed
-
- Stefan N, Cusi K. A global view of the interplay between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10:284–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

