Large-Bore Mechanical Thrombectomy Versus Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis in the Management of Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: Primary Results of the PEERLESS Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39470698
- PMCID: PMC11789609
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.072364
Large-Bore Mechanical Thrombectomy Versus Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis in the Management of Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: Primary Results of the PEERLESS Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: There are a lack of randomized controlled trial data comparing outcomes of different catheter-based interventions for intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism.
Methods: PEERLESS is a prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial that enrolled 550 patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism with right ventricular dilatation and additional clinical risk factors randomized 1:1 to treatment with large-bore mechanical thrombectomy (LBMT) or catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT). The primary end point was a hierarchal win ratio composite of the following (assessed at the sooner of hospital discharge or 7 days after the procedure): (1) all-cause mortality, (2) intracranial hemorrhage, (3) major bleeding, (4) clinical deterioration and/or escalation to bailout, and (5) postprocedural intensive care unit admission and length of stay. Assessments at the 24-hour visit included respiratory rate, modified Medical Research Council dyspnea score, New York Heart Association classification, right ventricle/left ventricle ratio reduction, and right ventricular function. End points through 30 days included total hospital stay, all-cause readmission, and all-cause mortality.
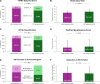
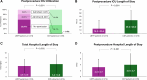
Results: The primary end point occurred significantly less frequently with LBMT compared with CDT (win ratio, 5.01 [95% CI, 3.68-6.97]; P<0.001). There were significantly fewer episodes of clinical deterioration and/or bailout (1.8% versus 5.4%; P=0.04) with LBMT compared with CDT and less postprocedural intensive care unit use (P<0.001), including admissions (41.6% versus 98.6%) and stays >24 hours (19.3% versus 64.5%). There were no significant differences in mortality, intracranial hemorrhage, or major bleeding between strategies or in a secondary win ratio end point including the first 4 components (win ratio, 1.34 [95% CI, 0.78-2.35]; P=0.30). At the 24-hour visit, respiratory rate was lower for patients treated with LBMT (18.3±3.3 versus 20.1±5.1; P<0.001), and fewer had moderate to severe modified Medical Research Council dyspnea scores (13.5% versus 26.4%; P<0.001), New York Heart Association classifications (16.3% versus 27.4%; P=0.002), and right ventricular dysfunction (42.1% versus 57.9%; P=0.004). Right ventricle/left ventricle ratio reduction was similar (0.32±0.24 versus 0.30±0.26; P=0.55). Patients treated with LBMT had shorter total hospital stays (4.5±2.8 overnights versus 5.3±3.9 overnights; P=0.002) and fewer all-cause readmissions (3.2% versus 7.9%; P=0.03), whereas 30-day mortality was similar (0.4% versus 0.8%; P=0.62).
Conclusions: PEERLESS met its primary end point in favor of LBMT compared with CDT in treatment of intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. LBMT had lower rates of clinical deterioration and/or bailout and postprocedural intensive care unit use compared with CDT, with no difference in mortality or bleeding.
Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT05111613.
Keywords: percutaneous aspiration; pulmonary embolism; randomized controlled trial; thrombectomy; thrombolytic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Jaber reports research grant/funding from Inari Medical, Medtronic, and Thrombolex; consultant fees from Abbott, Inari Medical, and Medtronic; and advisory board membership with Thrombolex. Dr Gonsalves reports research grant/funding from Inari Medical and consultant fees from Inari Medical. Dr Stortecky reports institutional research grants from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic, as well as consultant fees from Inari Medical. Dr Horr reports consultant fees from Argon, BD, Boston Scientific, Cook, Cordis, Inari Medical, Medtronic, and Penumbra. Dr Pappas reports research grant/funding from Inari Medical and consultant fees from Abiomed, Boston Scientific, Inari Medical, Medtronic, and Zoll. Dr Gandhi reports consultant fees from Argon, BD, Boston Scientific, Cook, Cordis, Inari Medical, Medtronic, and Penumbra. Dr Giri reports research grant/funding from Edwards Lifesciences and Inari Medical; consultant fees from Boston Scientific and Inari Medical; honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences; equity ownership in Endovascular Engineering; and advisory board membership with Boston Scientific. Dr Khandhar reports consultant fees from Inari Medical and Neptune Medical. Dr Lasorda reports consultant fees from Cardiovascular Systems Inc, Edwards Lifesciences, and Shockwave Medical. Dr Dexter reports consultant fees from AngioDynamics, Boston Scientific, Inari Medical, and Penumbra. Dr Azene reports research grant/funding from Endovascular Engineering and Inari Medical; consultant fees from Medtronic and Philips; and honoraria from Philips. Dr Campbell reports consultant fees from Inari Medical. Dr Lindquist reports research grant/funding from Adient Medical, AstraZeneca, GE, Inari Medical, Philips, and Sirtex; consultant fees from Boston Scientific, EndoShape Inc, Inari Medical, Philips, and TriSalus Life Sciences; honoraria from Boston Scientific and Inari Medical; and advisory board membership with Boston Scientific, Inari Medical, and TriSalus Life Sciences. Dr Raskin reports consultant fees from Abbott Medical, Abiomed, Imperative Care, and Inari Medical. Dr Hernandez reports advisory board membership with Philips. Dr Rali reports research grant/funding from Janssen, ThinkSono, Thrombolex, and Viz.AI; consultant fees from AIDOC, Inari Medical, Penumbra, ThinkSono, Thrombolex, and Viz.AI; honoraria from Janssen; and advisory board membership with Inari Medical and Thrombolex. Dr Bruckel reports research grants/funding from Inari Medical; consultant fees from Asahi Intecc Medical; and honoraria from Medtronic. Dr Camacho reports research grants/funding from Elestra and TriSalus Life Sciences; consultant fees from Pulse Biosciences and TriSalus Life Sciences; honoraria from Wolters Kluwer (SIO, CIO). Dr Toma reports consultant fees from Neptune Medical. Dr Basra reports consultant fees from Abbott, AngioDynamics, and Lexicon. Dr Bergmark reports research grants/funding from Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Inari Medical, Ionis, Pfizer, and Philips, as well as advisory board membership with Boston Scientific. Dr O’Connor reports research grants/funding from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Silk Road and consultant fees from Philips. Dr Gibson reports consultant support to spouse from Inari Medical. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures

Comment in
-
A Win for Clinical Evidence: The First Head-to-Head Trial of Interventional Strategies for the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism.Circulation. 2025 Feb 4;151(5):274-276. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.072972. Epub 2025 Feb 3. Circulation. 2025. PMID: 39899637 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wendelboe AM, Raskob GE. Global burden of thrombosis: epidemiologic aspects. Circ Res. 2016;118:1340–1347. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306841 - PubMed
-
- Zghouzi M, Mwansa H, Shore S, Hyder SN, Kamdar N, Moles VM, Barnes GD, Froehlich J, McLaughlin VV, Paul TK, et al. Sex, racial, and geographic disparities in pulmonary embolism-related mortality nationwide. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20:1571–1577. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202302-091OC - PubMed
-
- Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C, Bueno H, Geersing GJ, Harjola VP, Huisman MV, Humbert M, Jennings CS, Jimenez D, et al. ; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur Heart J. 2020;41:543–603. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz405 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

