Prevalence of Breast Cancer Screening in Asia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39471004
- PMCID: PMC11711340
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.10.3379
Prevalence of Breast Cancer Screening in Asia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality among women above 50 years of age. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed at identifying the prevalence and trend of breast cancer screening among selected Asian countries.
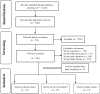
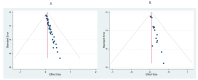
Methods: We searched three databases including, PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus using our search terms. Two independent reviewers screened titles and abstracts applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria specified in the PROSPERO (registration ID: CRD42023401516) and any conflicts were resolved through discussion. Two independent reviewers and conflicts also completed the full-text screening, which was solved. Relevant information was extracted in an Excel sheet and random effects meta-analysis was performed to identify the pooled estimate of breast cancer screening in Asia using Stata 17.
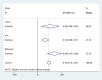
Results: We identified 41 studies from 14 selected Asian countries reporting breast cancer screening rates from 2012-2023. The pooled estimate of four countries (China, Iran, Japan, and Korea) with more than three data points on clinical breast examination and mammographic screening showed a screening rate of 24% (95% CI: 0.20 - 0.27) and 18% (95% CI: (0.14 - 0.21) in the last ten years respectively.
Conclusion: Most Asian countries do not have sufficient data on breast cancer screening due to a lack of nationally representative surveys or national-level cancer registries. Therefore, it is crucial to strengthen cancer control policies including breast cancer screening programs.
Keywords: ANCCA; Asia; Meta-analysis; Screening; breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare. The authors have no potential financial, personal, or other conflicts of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Performance of a subsidised mammographic screening programme in Malaysia, a middle-income Asian country.BMC Public Health. 2017 Jan 28;17(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4015-3. BMC Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28129762 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of promoting prevention and the early detection of breast cancer among women, a hospital-based education and screening interventions in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review protocol.Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 14;7(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s13643-018-0889-0. Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30547842 Free PMC article.
-
Patient preferences for breast cancer screening: a systematic review update to inform recommendations by the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care.Syst Rev. 2024 May 28;13(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02539-8. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38807191 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer Screening in Women With Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Psychiatr Serv. 2020 Mar 1;71(3):263-268. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201900318. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Psychiatr Serv. 2020. PMID: 31722645 Free PMC article.
-
Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;17(2):e1173. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1173. eCollection 2021 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 37131927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative study of early onset cancer burden between China and the United States from 1990 to 2021.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 5;15(1):28527. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10185-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40764701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer. World Health Organization; 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer .
-
- World Health Organization. The global breast cancer initiative framework. WHO. World Health Organization; 2022. [ Accessed March 7 2024]. Available from: https://www.who.int/multi-media/details/global-breast-cancer-initiative-....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

