Medicinal Plants Derived Green Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Potential Applications in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 39471005
- PMCID: PMC11711356
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.10.3393
Medicinal Plants Derived Green Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Potential Applications in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
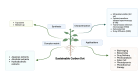
Objective: This review aims to explore the synthesis, characterization, and potential applications of carbon dots (CDs) derived from medicinal plants for cancer prevention, highlighting their role as a promising alternative in nanotechnological approaches.
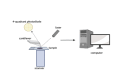
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted to gather information on the synthesis methods, complex matrices, characterization techniques, and potential applications of CDs derived from medicinal plants in cancer therapy.
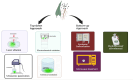
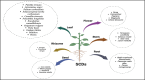
Result: Carbon dots (CDs) have emerged as a subject of significant interest due to their favorable chemical and biological properties. Various precursors, including graphite, carbon black, and organic molecules, are utilized in the synthesis of CDs through chemical or physical methods. Notably, CDs derived from medicinal plants offer environmentally friendly alternatives, leveraging complex matrices such as aqueous, alcoholic, and hydroalcoholic extracts. This review emphasizes the green synthesis approaches, characterization techniques, and diverse applications of CDs, including drug transport, bioimaging, biosensing, and anti-cancer therapies. Furthermore, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of different synthesis methods, aiding researchers in selecting appropriate techniques for continuous production.
Conclusion: Carbon dots (CDs) represent a transformative advancement in nanotheranostics, offering a versatile platform for precise cancer diagnosis and therapy. With inherent anticancer properties, CDs hold promise in photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT), enabling precise tumor targeting while minimizing systemic toxicity. To address the limitations of standalone PDT and PTT, researchers are exploring multimodal treatment approaches integrating CDs. By leveraging the unique properties of CDs derived from medicinal plants, a new era of precision cancer therapy may be realized, emphasizing enhanced therapeutic outcomes and reduced adverse effects.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Complex Matrices; Green Synthesis; Medicinal plant; Nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The future of plant based green carbon dots as cancer Nanomedicine: From current progress to future Perspectives and beyond.J Adv Res. 2025 Jan;67:133-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.01.034. Epub 2024 Feb 5. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38320729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties and Biomedical Applications.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jan 2;14(1):27. doi: 10.3390/jfb14010027. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36662074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecules derived carbon dots: synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine.J Nanobiotechnology. 2019 Aug 26;17(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12951-019-0525-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019. PMID: 31451110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in waste-derived carbon dots and their nanocomposites for environmental remediation and biological applications.Environ Res. 2024 Jun 15;251(Pt 1):118560. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118560. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38447603 Review.
-
Advancements of carbon dots: From the perspective of medicinal chemistry.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Dec 15;280:116931. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116931. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39369486 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of L-DOPA in neurological and neurodegenerative complications: a review.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun 9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05324-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40488810 Review.
-
Research progress on the preparation, performance, mechanisms, and applications of carbon nanomaterials against Gram-negative bacteria.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 30;15(28):22180-22201. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01704a. eCollection 2025 Jun 30. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40599578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu X, Ray R, Gu Y, Ploehn HJ, Gearheart L, Raker K, et al. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126(40):12736–7. - PubMed
-
- Jaleel JA, Pramod K. Artful and multifaceted applications of carbon dot in biomedicine. J Control Release. 2018;269:302–21. - PubMed
-
- Sun YP, Zhou B, Lin Y, Wang W, Fernando KS, Pathak P, et al. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128(24):7756–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

