Heavier Diferrocenylpnictogenium Ions
- PMID: 39471106
- PMCID: PMC11711300
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202403555
Heavier Diferrocenylpnictogenium Ions
Abstract
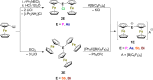
The synthesis, characterization and reactivity of the diferrocenylphosphenium ion [Fc2P]+ was extended to the heavier diferrocenylpnictogenium ions, [Fc2E]+ (E=As, Sb, Bi). The lighter diferrocenylnitrenium ion, [Fc2N]+, was detected by mass spectrometry, but could not be isolated. The molecular structures of [Fc2E]+ (E=P, As, Sb, Bi) reveal intramolecular coordination of the iron atoms, which counterbalance the electron deficiency of the pnictogens without affecting the strong Lewis acidities, which were determined according to the method of Gutmann and Beckett. The (electro-)chemical oxidation and reduction afforded the dications [Fc2E]2+ (E=P (unstable), As) and the neutral dipnictogens Fc2EEFc2 (E=P, As).
Keywords: Carbene analogues; Cations; Ferrocene; Lewis acids; Pnictogenium ions.
© 2024 The Author(s). Chemistry - A European Journal published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- Riddlestone I. M., Kraft A., Schaefer J., Krossing I., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13982–14024. - PubMed
-
- Cais M., Organomet. Chem. Rev. 1966, 1, 435–454.
-
- Luoan S., Kapon M., Cais M., Herbstein F. H., Angew. Chem. 1972, 84, 1104–1106.
-
- Cais M., Dani S., Herbstein F., Kapon M., J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 5554–5558.
-
- Behrens U., J. Organomet. Chem. 1979, 182, 89–98.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

