Cracking the Code of the Jugular Vagal Sensory Neurons in Allergic Airway Responsiveness
- PMID: 39471332
- PMCID: PMC12005020
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0445ED
Cracking the Code of the Jugular Vagal Sensory Neurons in Allergic Airway Responsiveness
Figures
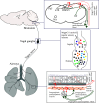
Comment on
-
MrgprC11+ Jugular Neurons Control Airway Hyperresponsiveness in Allergic Airway Inflammation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025 Apr;72(4):393-407. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0153OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39405479 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

