Internal regulation between constitutively expressed T cell co-inhibitory receptors BTLA and CD5 and tolerance in recent thymic emigrants
- PMID: 39471840
- PMCID: PMC11521602
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.240178
Internal regulation between constitutively expressed T cell co-inhibitory receptors BTLA and CD5 and tolerance in recent thymic emigrants
Abstract
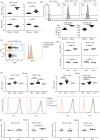
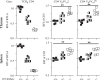
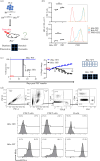
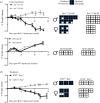
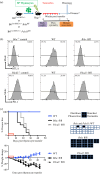
Immunologic self-tolerance involves signals from co-inhibitory receptors. Several T cell co-inhibitors, including PD-1, are expressed upon activation, whereas CD5 and BTLA are expressed constitutively. The relationship between constitutively expressed co-inhibitors and when they are needed is unknown. Deletion of Btla demonstrated BTLA regulates CD5 expression. Loss of BTLA signals, but not signalling by its ligand, HVEM, leads to increased CD5 expression. Higher CD5 expression set during thymic selection is associated with increased self-recognition, suggesting that BTLA might be needed early to establish self-tolerance. We found that BTLA and PD-1 were needed post-thymic selection in recent thymic emigrants (RTE). RTE lacking BTLA caused a CD4 T cell and MHC class II dependent multi-organ autoimmune disease. Together, our findings identify a negative regulatory pathway between two constitutively expressed co-inhibitors, calibrating their expression. Expression of constitutive and induced co-inhibitory receptors is needed early to establish tolerance in the periphery for RTE.
Keywords: BTLA; CD5; T cells; autoimmunity; recent thymic emigrants; tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
L.B. is CSO and board member at JJP Biologics, a company developing HVEM targeting approaches in oncology.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
