Intrauterine infusion of autologous platelet rich plasma can be an efficient treatment for patients with unexplained recurrent implantation failure
- PMID: 39472511
- PMCID: PMC11522411
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77578-1
Intrauterine infusion of autologous platelet rich plasma can be an efficient treatment for patients with unexplained recurrent implantation failure
Abstract
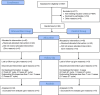
The studies posits that there is not sufficient evidence to support the use of intrauterine platelet-rich plasma (PRP) infusion in patients with recurrent implantation failure (RIF). This study aims to investigate the effects of infusion of PRP on patients with unexplained-RIF in fresh and frozen embryo transfer (ET) cycles. A total of 80 participants were included in this study. The participants were randomly assigned to one of two groups with and without PRP infusion. Each of the PRP and control groups were also divided into fresh and frozen ET subgroups. ET outcomes were compared between groups. Clinical pregnancy rate was significantly higher in Frozen ET in PRP group than other subgroups (p < 0.0001). Miscarriage rate were significantly lower in PRP group than control group. Pregnancy complications and preterm labor were significantly higher in PRP group than control group (p < 0.0001). Live birth and healthy baby rate were significantly higher in PRP group than control group (p < 0.0001). The intrauterine infusion of 0.8-1 ml of PRP 48 h before blastocyst ET at fresh and frozen cycles can be an efficient treatment option for u-RIF patients. Also, results indicated that the clinical pregnancy rate was equal to the live birth rate at fresh ET cycles, whereas the live birth rate was lower than the clinical pregnancy rate at frozen ET cycles. Therefore, considering the superiority of fresh cycles over freeze cycles, the infusion of PRP into the uterus of patients with RIF is recommended to be done at fresh ET cycles.Trial registration: NCT, NCT03996837. Registered 25/06/2019. Retrospectively registered, http://www.clinicaltrial.gov/ NCT03996837.
Keywords: Fresh embryo transfer; Frozen embryo transfer; Platelet-rich plasma; Pregnancy outcome; Recurrent implantation failure; Unexplained infertility.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiogenic factor-driven improvement of refractory thin endometrium with autologous platelet-rich plasma intrauterine infusion in frozen embryo transfer cycles.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 3;15:1431453. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1431453. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39290323 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of autologous platelet-rich plasma intrauterine perfusion on clinical outcomes in recurrent implantation failure patients with non-thin endometrium undergoing frozen-thawed embryo transfer.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025 May;311(5):1423-1433. doi: 10.1007/s00404-025-07983-y. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 40105934 Free PMC article.
-
Improved in vitro fertilization success and pregnancy outcome with autologous platelet-rich plasma treatment in unexplained infertility patients that had repeated implantation failure history.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2019 Sep;35(9):815-818. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2019.1597344. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30966843
-
What is the impact of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in subcutaneous injection or intrauterine infusion and during both the fresh and frozen embryo transfer cycles on recurrent implantation failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis?Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Aug 13;19(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00810-4. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34388994 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma for women with recurrent implantation failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2023 Dec;43(1):2144177. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2022.2144177. Epub 2022 Nov 17. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2023. PMID: 36397660
Cited by
-
Add-On Technologies That Aim to Improve Oocyte Quality and Embryo Implantation Potential.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Feb 20;61(3):367. doi: 10.3390/medicina61030367. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40142178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deng, H., Wang, S., Li, Z., Xiao, L. & Ma, L. Effect of intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma for women with recurrent implantation failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol.43(1), 2144177 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Genest, G. et al. Immunomodulation for unexplained recurrent implantation failure: Where are we now? Reproduction165(2), R39–R60 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials