Xeroderma pigmentosum protein XPD controls caspase-mediated stress responses
- PMID: 39472562
- PMCID: PMC11522282
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53755-8
Xeroderma pigmentosum protein XPD controls caspase-mediated stress responses
Abstract
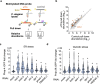
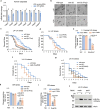
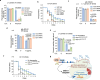
Caspases regulate and execute a spectrum of functions including cell deaths, non-apoptotic developmental functions, and stress responses. Despite these disparate roles, the same core cell-death machinery is required to enzymatically activate caspase proteolytic activities. Thus, it remains enigmatic how distinct caspase functions are differentially regulated. In this study, we show that Xeroderma pigmentosum protein XPD has a conserved function in activating the expression of stress-responsive caspases in C. elegans and human cells without triggering cell death. Using C. elegans, we show XPD-1-dependent activation of CED-3 caspase promotes survival upon genotoxic UV irradiation and inversely suppresses responses to non-genotoxic insults such as ER and osmotic stressors. Unlike the TFDP ortholog DPL-1 which is required for developmental apoptosis in C. elegans, XPD-1 only activates stress-responsive functions of caspase. This tradeoff balancing responses to genotoxic and non-genotoxic stress may explain the seemingly contradictory nature of caspase-mediated stress resilience versus sensitivity under different stressors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ellis, H. M. & Horvitz, H. R. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell44, 817–829 (1986). - PubMed
-
- Yuan, J. Y. & Horvitz, H. R. The Caenorhabditis elegans genes ced-3 and ced-4 act cell autonomously to cause programmed cell death. Dev. Biol.138, 33–41 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Yuan, J., Shaham, S., Ledoux, S., Ellis, H. M. & Horvitz, H. R. The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell75, 641–652 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Dick, S. A. et al. Caspase 3 cleavage of Pax7 inhibits self-renewal of satellite cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA112, E5246–E5252, https://doi.org/1512869112 (2015). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

