Clinical efficacy of intracavernous injection of platelet lysate for erectile dysfunction
- PMID: 39472866
- PMCID: PMC11520801
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-024-01633-2
Clinical efficacy of intracavernous injection of platelet lysate for erectile dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Among the emerging treatments for erectile dysfunction (ED), platelet-rich plasma (PRP), known for its ability to enhance tissue repair and regeneration, stands out as a promising therapeutic approach. In this innovative study, we aimed to assess the efficacy of intracavernous injections of platelet lysate (PL), a derivative of PRP, in improving erectile function among ED patients.
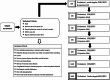
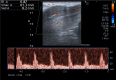
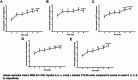
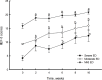
Methods: We enrolled twenty-six patients, aged between 35 and 70 years (mean age 51.6 ± 11.3 years), who had been experiencing ED for over six months and had an International Index of Erectile Function-5 (IIEF-5) score of 21 or less. Participants received autologous PL injections intracavernously every two weeks for a total of five administrations. We assessed Erection Hardness Score (EHS) and International Index of Erectile Function-5 (IIEF-5) bi-weekly for 16 weeks and conducted penile Doppler ultrasounds pre- and post-treatment to record peak systolic velocity (PSV) and resistance index (RI).
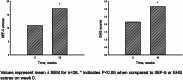
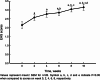
Results: Before treatment, the mean EHS was 2.15 ± 0.88 and IIEF-5 was 10.92 ± 5.28. Remarkable improvements were observed post-treatment, with the EHS significantly increasing to 3.15 ± 0.83 (p < 0.05) and IIEF-5 to 17.23 ± 5.26 (p < 0.05). Penile Doppler ultrasound exhibited an increase in both PSV and RI post-treatment, with the rise in RI being statistically significant.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that intracavernous injections of PL substantially enhance erectile function, as evidenced by improvements in EHS, IIEF-5, and the RI of penile Doppler ultrasound, without hemorrhagic events or other adverse reactions apart from temporary pain at the injection site during the 16-week follow-up period. These encouraging results suggest that PL injections are a safe and effective treatment modality for patients with moderate ED, potentially providing a less invasive and more physiologically friendly alternative to current ED management strategies.
Trial registration: The study received approval from the Institutional Review Board of National Taiwan University Hospital (IRB Number 202008061RIPC, date of registration 08/28/2020).
Keywords: Erectile dysfunction; Intracavernous injection; Platelet lysate; Platelet-rich plasma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Zamani M, Yaghoubi Y, Movassaghpour A, Shakouri K, Mehdizadeh A, Pishgahi A, et al. Novel therapeutic approaches in utilizing platelet lysate in regenerative medicine: are we ready for clinical use? J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):17172–86. - PubMed
-
- Alkandari MH, Touma N, Carrier S. Platelet-Rich plasma injections for Erectile Dysfunction and Peyronie’s Disease: a systematic review of evidence. Sex Med Rev. 2022;10(2):341–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

