Effect of surfactants on the stability and solar thermal absorption characteristics of water-based nanofluids with multi-walled carbon nanotubes
- PMID: 39473438
- PMCID: PMC11520205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.01.141
Effect of surfactants on the stability and solar thermal absorption characteristics of water-based nanofluids with multi-walled carbon nanotubes
Abstract
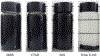
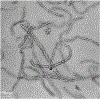
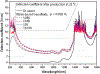
This paper reports the effect of various surfactants on the suspension stability and the solar thermal absorption characteristics of water-based nanofluids containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) that can be used as working fluids for volumetric solar thermal receivers. The water-based MWCNT nanofluids were prepared using a two-step method with four commonly used surfactants: sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS), cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and Triton X-100 (TX-100). The stability of the four surfactant-treated nanofluids was analyzed for over a month with an in-house developed laser transmission system. The effect of temperature on the stability of the nanofluid/surfactant mixtures was also examined. In addition, to identify the absorption characteristics of the four nanofluids, the spectral extinction coefficients were measured using an UV-Vis-NIR spectrophotometer. The absorbed sunlight fraction was calculated using the measured spectral extinction coefficient, which enabled an evaluation of the absorption characteristics of the nanofluids. The MWCNT nanofluids were clearly shown to enhance the absorption rate of solar thermal energy. The suspension stability and the absorption characteristics were also strongly affected by the type of surfactant. Moreover, using the absorbed sunlight fraction and suspension-stability factor, we experimentally show the relation between the absorption characteristics and suspension stability in nanofluids.
Keywords: Absorbed sunlight fraction; Extinction coefficient; MWCNTs; Surfactants; Suspension stability; Volumetric solar thermal receivers; Water-based nanofluids containing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Kalogious SA, Solar thermal collectors and applications, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci 30 (2004) 231–295.
-
- Tian Y, Zhao CY, A review of solar collectors and thermal energy storage in solar thermal applications, Appl. Energy 104 (2013) 538–553.
-
- Lee SH, Jang SP, Extinction coefficient of aqueous nanofluids containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf 67 (2013) 930–935.
-
- Sani E, Barison S, Pagura C, Mercatelli L, Sansoni P, Fontani D, Jafrancesco D, Francini F, Carbon nanohorns-based nanofluids as direct sunlight absorbers, Opt. Express 18 (2010) 5179–5187. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
