Quantitative, real-time imaging of spreading depolarization-associated neuronal ROS production
- PMID: 39473491
- PMCID: PMC11519816
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1465531
Quantitative, real-time imaging of spreading depolarization-associated neuronal ROS production
Abstract
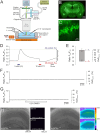
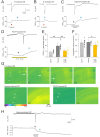
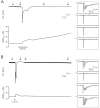
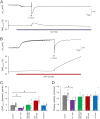
Spreading depolarization (SD) causes a massive neuronal/glial depolarization, disturbs ionic homeostasis and deranges neuronal network function. The metabolic burden imposed by SD may also generate marked amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Yet, proper optical tools are required to study this aspect with spatiotemporal detail. Therefore, we earlier generated transgenic redox indicator mice. They express in excitatory projection neurons the cytosolic redox-sensor roGFP, a reduction/oxidation sensitive green fluorescent protein which is ratiometric by excitation and responds reversibly to redox alterations. Using adult male roGFPc mice, we analyzed SD-related ROS production in CA1 stratum pyramidale of submerged slices. SD was induced by K+ microinjection, O2 withdrawal or mitochondrial uncoupling (FCCP). The extracellular DC potential deflection was accompanied by a spreading wavefront of roGFP oxidation, confirming marked neuronal ROS generation. Hypoxia-induced SD was preceded by a moderate oxidation, which became intensified as the DC potential deflection occurred. Upon K+-induced SD, roGFP oxidation slowly recovered within 10-15 min in some slices. Upon FCCP-or hypoxia-induced SD, recovery was limited. Withdrawing extracellular Ca2+ markedly dampened the SD-related roGFP oxidation and improved its reversibility, confirming a key-role of neuronal Ca2+ load in SD-related ROS generation. Neither mitochondrial uncoupling, nor inhibition of NADPH oxidase or xanthine oxidase abolished the SD-related roGFP oxidation. Therefore, ROS generation during SD involves mitochondria as well as non-mitochondrial sources. This first-time analysis of SD-related ROS dynamics became possible based on quantitative redox imaging in roGFP mice, an advanced approach, which will contribute to further decipher the molecular understanding of SD in brain pathophysiology.
Keywords: mitochondria; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; redox imaging; roGFP; spreading depression.
Copyright © 2024 Ackermann, Buchholz, Dietrich and Müller.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

