The genome sequence of a bluebottle fly, Calliphora vicina (Linnaeus, 1758)
- PMID: 39473873
- PMCID: PMC11519611
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.22469.1
The genome sequence of a bluebottle fly, Calliphora vicina (Linnaeus, 1758)
Abstract
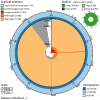
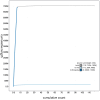
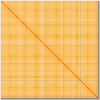
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Calliphora vicina (bluebottle blow fly; Arthropoda; Insecta; Diptera; Calliphoridae). The genome sequence is 706.5 megabases in span. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into 6 chromosomal pseudomolecules, including the X sex chromosome. The mitochondrial genome has also been assembled and is 16.72 kilobases in length. Gene annotation of this assembly on Ensembl identified 13,436 protein coding genes.
Keywords: Calliphora vicina; Diptera; bluebottle blow fly; chromosomal; genome sequence.
Copyright: © 2024 Sivell O et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The genome sequence of a bluebottle, Calliphora vomitoria (Linnaeus, 1758).Wellcome Open Res. 2023 Feb 21;8:93. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.18891.1. eCollection 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023. PMID: 38173563 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of a conopid fly, Myopa testacea (Linnaeus, 1767).Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Feb 29;9:99. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.20647.1. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 38689759 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of a woodlouse fly, Melanophora roralis (Linnaeus, 1758).Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Oct 30;9:637. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.23295.1. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39659996 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the dark-edged bee fly, Bombylius major (Linnaeus, 1758).Wellcome Open Res. 2023 Sep 1;8:379. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.19804.1. eCollection 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023. PMID: 38533437 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of a tachinid fly, Nowickia ferox (Panzer, 1809).Wellcome Open Res. 2023 Jun 23;8:275. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.19575.1. eCollection 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023. PMID: 38919871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson GS: Minimum and maximum development rates of some forensically important calliphoridae (Diptera). J Forensic Sci. 2000;45(4):824–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

