Machine learning-based radiomics in neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular disease
- PMID: 39473906
- PMCID: PMC11518692
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.778
Machine learning-based radiomics in neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular disease
Abstract
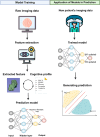
Cognitive impairments, which can be caused by neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular disease, represent a growing global health crisis with far-reaching implications for individuals, families, healthcare systems, and economies worldwide. Notably, neurodegenerative-induced cognitive impairment often presents a different pattern and severity compared to cerebrovascular-induced cognitive impairment. With the development of computational technology, machine learning techniques have developed rapidly, which offers a powerful tool in radiomic analysis, allowing a more comprehensive model that can handle high-dimensional, multivariate data compared to the traditional approach. Such models allow the prediction of the disease development, as well as accurately classify disease from overlapping symptoms, therefore facilitating clinical decision making. This review will focus on the application of machine learning-based radiomics on cognitive impairment caused by neurogenerative and cerebrovascular disease. Within the neurodegenerative category, this review primarily focuses on Alzheimer's disease, while also covering other conditions such as Parkinson's disease, Lewy body dementia, and Huntington's disease. In the cerebrovascular category, we concentrate on poststroke cognitive impairment, including ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, with additional attention given to small vessel disease and moyamoya disease. We also review the specific challenges and limitations when applying machine learning radiomics, and provide our suggestion to overcome those limitations towards the end, and discuss what could be done for future clinical use.
Keywords: machine learning; neuroimaging; poststroke cognitive impairment; radiomics; stroke.
© 2024 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Rost NS, Brodtmann A, Pase MP, et al. Post‐stroke cognitive impairment and dementia. Circ Res. 2022;130(8):1252‐1271. - PubMed
-
- Hu HY, Ou YN, Shen XN, et al. White matter hyperintensities and risks of cognitive impairment and dementia: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of 36 prospective studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;120:16‐27. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
