Recent advances in copper homeostasis-involved tumor theranostics
- PMID: 39474127
- PMCID: PMC11513462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2024.100948
Recent advances in copper homeostasis-involved tumor theranostics
Abstract
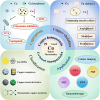
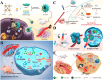
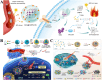
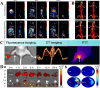
As the third essential trace element in the human body, copper plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, which lays the foundation for its broad applications in cancer treatments. The overview of copper, including pharmacokinetics, signaling pathways, and homeostasis dysregulation, is hereby discussed. Additionally, cuproptosis, as a newly proposed cell death mechanism associated with copper accumulation, is analyzed and further developed for efficient cancer treatment. Different forms of Cu-based nanoparticles and their advantages, as well as limiting factors, are introduced. Moreover, the unique characteristics of Cu-based nanoparticles give rise to their applications in various imaging modalities. In addition, Cu-based nanomaterials are featured by their excellent photothermal property and ROS-associated tumor-killing potential, which are widely explored in diverse cancer therapies and combined therapies. Reducing the concentration of Cu2+/Cu+ is another cancer-killing method, and chelators can meet this need. More importantly, challenges and future prospects are identified for further research.
Keywords: Chelators; Copper homeostasis; Cu-based nanoparticles; Cuproptosis; Tumor theranostics.
© 2024 Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Makhdoumi P., Karimi H., Khazaei M. Review on metal-based nanoparticles: role of reactive oxygen species in renal toxicity. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020;33(10):2503–2514. - PubMed
-
- Xie W., Guo Z., Zhao L., Wei Y. The copper age in cancer treatment: from copper metabolism to cuproptosis. Prog. Mater Sci. 2023;138
-
- Wang X., Zhou M., Liu Y., Si Z. Cope with copper: from copper linked mechanisms to copper-based clinical cancer therapies. Cancer Lett. 2023;561 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

