Clinical features and in-hospital mortality predictors of concurrent cardio-cerebral infarction: insights from a dual-center retrospective study
- PMID: 39474370
- PMCID: PMC11520769
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1465144
Clinical features and in-hospital mortality predictors of concurrent cardio-cerebral infarction: insights from a dual-center retrospective study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to enhance the understanding of cardio-cerebral infarction (CCI) clinical features and identify key prognostic factors, thereby providing an empirical foundation for advancing prevention and treatment strategies and ultimately improving clinical outcomes for CCI patients.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 17,645 AIS and 7,584 AMI patients admitted to two hospitals from 2014 to 2023. Univariate analysis, Spearman correlation, and multivariate logistic regression were performed to identify independent risk factors. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine optimal cutoff values.
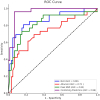
Results: This study enrolled 85 patients with CCI, representing an overall CCI incidence of approximately 0.34%. Males comprised 64.71% of the cohort. ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and cardiogenic cerebral infarction were the most predominant subtypes. The in-hospital mortality rate was 30.59%, with 65.38% of deaths attributed to cardiac causes. Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified three independent risk factors for in-hospital mortality: elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), decreased serum albumin, and increased peak N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels (NT-proBNP). ROC curve analysis demonstrated that the area under the curve (AUC) for the NLR, albumin concentration and peak NT-proBNP concentration were 0.863, 0.723, and 0.824, respectively. The optimal cutoff values were 6.914 for NLR, 33.80 g/L for albumin, and 9474.50 pg/mL for peak NT-proBNP. The AUC of the combined diagnostic model reached 0.959, significantly outperforming the individual indicators.
Conclusion: Elevated NLR, decreased serum albumin, and increased peak NT-proBNP levels independently predict in-hospital mortality in CCI patients. Combining these biomarkers enhances predictive capability for adverse outcomes.
Keywords: N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; albumin; cardio-cerebral infarction; in-hospital mortality; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Copyright © 2024 Gao, Yu, Jin, Cai, Fang, Wang, Yang, Chen, Ye and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chinese Society of Cardiology of Chinese Medical Association; Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiology . Chinese Society of Cardiology (CSC) guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. (2019) 2019:766–83. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2019.10.003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

