Reinvesting the cellular properties of human amniotic epithelial cells and their therapeutic innovations
- PMID: 39474414
- PMCID: PMC11518714
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466529
Reinvesting the cellular properties of human amniotic epithelial cells and their therapeutic innovations
Abstract
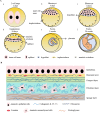
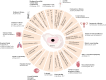
Human amniotic epithelial cells (hAECs) have shown promising therapeutic effects in numerous studies on various diseases due to their properties such as low immunogenicity, immunomodulation, paracrine effect, and no teratoma formation in vivo. Nevertheless, there are still many problems in archiving the large-scale clinical application of hAECs, ranging from the vague definition of cell properties to the lack of clarification of the motion of actions in cell therapies, additionally, to the gap between cell quantities with limited proliferation capacity. This review provides a detailed overview of hAECs in the aspects of the lineage development of amniotic epithelial cell, cell characteristics and functional roles, ex vivo cell cultivation and expansion systems, as well as their current status and limitations in clinical applications. This review also discusses the advantages, limitations and feasibility of hAECs, and anticipates their prospects as cell therapy products, with the aim of further promoting their clinical applications.
Keywords: cell expansion; cell therapy; clinical trials; epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity (EMP); human amniotic epithelial cells (hAECs); therapeutic mechanisms.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Lu, Zhao, Luo, Hao, Zhang and He.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors JY, YL, JZ, YL, WH, WZ, and ZH were employed by the company Shanghai iCELL Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Scale-Up of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells Through Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity Under Defined Conditions.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(11):e2408581. doi: 10.1002/advs.202408581. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39804851 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey and Critical Evaluation of Isolation, Culture, and Cryopreservation Methods of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells.Cell Cycle. 2022 Apr;21(7):655-673. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.2020015. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 35289707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic differentiation of human amniotic epithelial cells and in vivo therapeutic effect on animal model of cirrhosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Nov;30(11):1673-82. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12991. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25973537
-
Therapeutic potential of hAECs for early Achilles tendon defect repair through regeneration.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018 Mar;12(3):e1594-e1608. doi: 10.1002/term.2584. Epub 2017 Nov 17. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018. PMID: 29024514
-
Stem cell characteristics and the therapeutic potential of amniotic epithelial cells.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2018 Oct;80(4):e13003. doi: 10.1111/aji.13003. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29956869 Review.
Cited by
-
Stem cell treatments for female reproductive disorders: a comprehensive review.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Jul 24;18(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01750-y. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 40708035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parolini O, Alviano F, Bagnara GP, Bilic G, Buhring HJ, Evangelista M, et al. . Concise review: isolation and characterization of cells from human term placenta: outcome of the first international Workshop on Placenta Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells. (2008) 26:300–11. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0594 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

