Immunoregulation role of the erythroid cells
- PMID: 39474425
- PMCID: PMC11518727
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466669
Immunoregulation role of the erythroid cells
Abstract
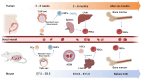
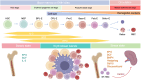
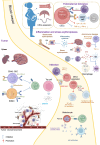
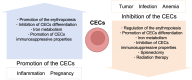
Erythroid cells are the most abundant cells in the human body. In addition to their established function in gas-transportation, erythroid cells at various stages of differentiation have recently been shown to have immunomodulatory roles. Red blood cells may serve as modulators of innate and adaptive immunity, while their immature counterparts, CD71+ erythroid cells (CECs) have important immunomodulatory functions in various contexts. CECs are abundant in human cord blood and placenta, where they contribute to fetomaternal tolerance. CECs also accumulate in patients with infections, tumors, and anemia, and effectively suppress T cells by producing high levels of arginase, reactive oxygen species, programmed death-ligand 1, transforming growth factor β, and/or interleukin-10. Here, we systematically summarize the immunomodulatory functions of erythroid cells and propose some potential therapeutic applications based on their characteristics.
Keywords: CD71 + erythroid cells; PD-L1; ROS; TGF-β; erythropoiesis; immunoregulation.
Copyright © 2024 Niu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Conway de Macario E, Macario AJ. Immunosuppression associated with erythropoiesis in genetic low responder mice. Ann Immunol (Paris). (1980) 131C:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Tsyrlova IG. Erythroid immunosuppressor cells (Er suppressors) and their role in the regulation of immunity. Vestn Akad Med Nauk SSSR. (1991) 12:34–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

