Making the effect visible - OX40 targeting nanobodies for in vivo imaging of activated T cells
- PMID: 39474429
- PMCID: PMC11518761
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1480091
Making the effect visible - OX40 targeting nanobodies for in vivo imaging of activated T cells
Abstract
Purpose: Human OX40 (hOX40/CD134), a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, is mainly expressed on activated T lymphocytes. Triggered by its ligand OX40L (CD252), it provides costimulatory signals that support the differentiation, proliferation and long-term survival of T cells. Besides being a relevant therapeutic target, hOX40 is also an important biomarker for monitoring the presence or infiltration of activated T cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME), the inflammatory microenvironment (IME) in immune-mediated diseases (IMIDs) and the lymphatic organs. Here, we developed novel single domain antibodies (nanobodies, Nbs) targeting hOX40 to monitor the activation status of T cells by in vivo molecular imaging.
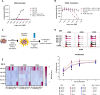
Methods: Nbs against hOX40 (hOX40-Nbs) were selected from an immunized Nb-library by phage display. The identified hOX40-Nbs were characterized in vitro, including determination of their specificity, affinity, stability, epitope recognition and their impact on OX40 signaling and T cell function. A lead candidate was site-specifically conjugated with a fluorophore via sortagging and applied for noninvasive in vivo optical imaging (OI) of hOX40-expressing cells in a xenograft mouse model.
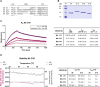
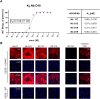
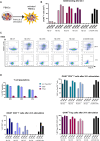
Results: Our selection campaign revealed four unique Nbs that exhibit strong binding affinities and high stabilities under physiological conditions. Epitope binning and domain mapping indicated the targeting of at least two different epitopes on hOX40. When analyzing their impact on OX40 signaling, an agonistic effect was excluded for all validated Nbs. Incubation of activated T cells with hOX40-Nbs did not affect cell viability or proliferation patterns, whereas differences in cytokine release were observed. In vivo OI with a fluorophore-conjugated lead candidate in experimental mice with hOX40-expressing xenografts demonstrated its specificity and functionality as an imaging probe.
Conclusion: Considering the need for advanced probes for noninvasive in vivo monitoring of T cell activation dynamics, we propose, that our hOX40-Nbs have a great potential as imaging probes for noninvasive and longitudinal in vivo diagnostics. Quantification of OX40+ T cells in TME or IME will provide crucial insights into the activation state of infiltrating T cells, offering a valuable biomarker for assessing immune responses, predicting treatment efficacy, and guiding personalized immunotherapy strategies in patients with cancer or IMIDs.
Keywords: OX40; T cell activation; in vivo imaging; monitoring immunotherapies; nanobody; tumor microenvironment (TME).
Copyright © 2024 Frecot, Blaess, Wagner, Kaiser, Traenkle, Fandrich, Jakobi, Scholz, Nueske, Schneiderhan-Marra, Gouttefangeas, Kneilling, Pichler, Sonanini and Rothbauer.
Conflict of interest statement
DF, DS, MK, BP, TW, BT, PK, and UR are named as inventors on a patent application claiming the use of the described nanobodies for diagnosis and therapeutics filed by the Natural and Medical Sciences Institute, the Werner Siemens Imaging Center and the University of Tuebingen. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of an agonistic aptamer against the T cell costimulatory receptor, OX40.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013 Feb;23(1):35-43. doi: 10.1089/nat.2012.0388. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013. PMID: 23113766 Free PMC article.
-
Domain binding and isotype dictate the activity of anti-human OX40 antibodies.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Dec;8(2):e001557. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001557. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33428585 Free PMC article.
-
SHR-1806, a robust OX40 agonist to promote T cell-mediated antitumor immunity.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2426305. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2426305. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39543823 Free PMC article.
-
OX40-OX40 ligand interaction in T-cell-mediated immunity and immunopathology.Adv Immunol. 2010;105:63-98. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(10)05003-0. Adv Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20510730 Review.
-
The significance of OX40 and OX40L to T-cell biology and immune disease.Immunol Rev. 2009 May;229(1):173-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00766.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19426222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanobodies targeting the tumor microenvironment and their formulation as nanomedicines.Mol Cancer. 2025 Mar 4;24(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02270-5. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40033293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

