A Patching and Coding Lipid Raft-Localized Universal Imaging Platform
- PMID: 39474480
- PMCID: PMC11503886
- DOI: 10.1021/cbmi.3c00109
A Patching and Coding Lipid Raft-Localized Universal Imaging Platform
Abstract
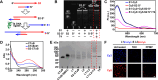
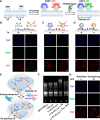
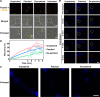
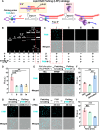
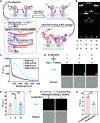
Lipid rafts (LRs) are relatively well-ordered functional microdomains in cell membranes and play an irreplaceable role in physiological processes as a transduction platform for multiple signaling pathways. Due to their small size and high spatiotemporal dynamics, it is difficult to perform lipid raft-localized biomolecule imaging on the surface of living cells. Here, we report a DNA nanotechnology-based platform for reversible manipulation and localized analysis of lipid rafts, which consists of two modules: "patching and coding probe pair" and "fishing probe". The probe pair is generated by modifying two different sets of connectable DNA structures on a lipid raft-specific protein. After recognizing lipid rafts, the two probes in close proximity are linked by a DNA ligase reaction to form a lipid raft identity (LR-ID) code. The LR-ID strand patches and stabilizes the lipid raft structure. Interestingly, the raft patches formed can be depatched by restriction endonucleases, providing the first reversible manipulation of the lipid raft structure in living cells. We also designed a "fishing probe" with a DNA hairpin structure using an aptamer that can specifically bind to the target. The probe can cascade the reaction to two input signals "LR-ID" and "target protein" to generate an "off-on" fluorescence switch, allowing imaging and dynamic monitoring of target proteins localized in lipid rafts. By encoding arbitrary targets (in the case of glycans) in lipid rafts, we have created a universal lipid raft-localized imaging platform. This work provides an integrated analytical and manipulative platform to reveal lipid rafts and associated signaling pathways at the molecular level.
© 2023 The Authors. Co-published by Nanjing University and American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
