Navigating Reproductive Care in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 39475080
- PMCID: PMC11523042
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae048
Navigating Reproductive Care in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
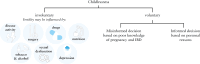
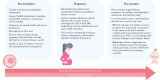
Inflammatory bowel disease [IBD] is often diagnosed in patients during their reproductive years. It is crucial that both healthcare providers and patients are adequately informed to avoid misguided decisions regarding family planning. One of the most important aspects during conception and pregnancy is to maintain disease remission, as disease activity is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Apart from methotrexate, most conventional drugs used in IBD are considered low risk during conception and pregnancy. For newer agents, evidence is still limited. If needed, surgery must not be postponed and should ideally be performed in specialized centres. In most patients, delivery should be vaginal except for patients with complex perianal disease, with an ileoanal pouch anastomosis, or if there is an obstetric contraindication. In children exposed to biological treatments during pregnancy, the risk of infections appears to be low, and psychomotor development is probably not affected. Regarding immunizations, the standard vaccination schedule for inactivated vaccines should be followed for children exposed to biologics in utero. In the case of live vaccines, such as rotavirus, decisions should be individualized and take into consideration the risk-benefit ratio, particularly in developing countries. In this review, we provide a comprehensive and updated overview of aspects related to fertility, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and the impact on the care of children born to mothers with IBD. Both the available evidence and areas of uncertainty are discussed, with the goal of assisting healthcare professionals caring for IBD patients during this important stage of their lives.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Fertility; breastfeeding; gestation; inflammatory bowel disease; lactation; offspring; pregnancy; ulcerative colitis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Conflict of interest statement
PS has served as speaker for Janssen and received Congress support from Janssen, Abbvie, Dr. Falk, Norgine, and Pfizer. JPG has served as a speaker, consultant, and advisory member for [or has received research funding from] MSD, Abbvie, Pfizer, Kern Pharma, Biogen, Mylan, Takeda, Janssen, Roche, Sandoz, Celgene/Bristol Myers, Gilead/Galapagos, Lilly, Ferring, Faes Farma, Shire Pharmaceuticals, Dr. Falk Pharma, Tillotts Pharma, Chiesi, Casen Fleet, Gebro Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Norgine, and Vifor Pharma. MJ has received research grants for other investigator-driven studies from Takeda, and the NOVO Nordisk Foundation [grant no. NNF23OC0081717], has received consultation fees from Ferring and Takeda, and has received speaker’s fees from Tillotts Pharma, MSD, Ferring, and Takeda. CPS has received unrestricted research grants from Warner Chilcott, Janssen, and AbbVie, has provided consultancy to Warner Chilcott, Dr Falk, AbbVie, Takeda, Fresenius Kabi, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Ferring, Arena, and Janssen, and had speaker arrangements with Warner Chilcott, Dr Falk, AbbVie, MSD, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, BMS, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Celltrion, and Takeda. MC has served as a speaker, as consultant or has received research or education funding from MSD, Abbvie, Hospira, Pfizer, Takeda, Janssen, Ferring, Shire Pharmaceuticals, Dr. Falk Pharma, Tillotts Pharma, Biogen, Lilly, and Gilead.
Figures
References
-
- Torres J, Chaparro M, Julsgaard M, et al. European Crohn’s and Colitis guidelines on sexuality, fertility, pregnancy, and lactation. J Crohns Colitis 2023;17:1–27. - PubMed
-
- Turner D, Ricciuto A, Lewis A, et al. ; International Organization for the Study of IBD. STRIDE-II: an update on the selecting therapeutic targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) Initiative of the International Organization for the Study of IBD (IOIBD): determining therapeutic goals for Treat-to-Target strategies in IBD. Gastroenterology 2021;160:1570–83. - PubMed
-
- Vieujean S, De Vos M, Paridaens K, Daftary GS, Danese S, Peyrin-Biroulet L.. Fertility and assisted reproductive technologies outcomes of women with non-surgically managed inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review. J Crohns Colitis 2023;17:614–32. - PubMed
-
- Zhao S, Wang J, Liu Y, et al. Inflammatory bowel diseases were associated with risk of sexual dysfunction in both sexes: a meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2019;25:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Friedman S. A meta-analysis of sexual function in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: examining a small piece of the puzzle. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2018;25:708–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

