Supplemental breast cancer screening after negative mammography in US women with dense breasts
- PMID: 39475439
- PMCID: PMC12145904
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djae272
Supplemental breast cancer screening after negative mammography in US women with dense breasts
Abstract
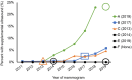
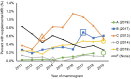
The extent and determinants of supplemental screening among women with dense breasts are unclear. We evaluated a retrospective cohort of 498 855 women aged 40-74 years with heterogeneously or extremely dense breasts who obtained 1 176 251 negative screening mammography examinations during 2011-2019 in the United States. Overall, 2.8% and 0.3% of mammograms had supplemental ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) within 1 year, respectively. Onsite availability was associated with ultrasound (odds ratio [OR] = 4.35, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 4.21 to 4.49) but not MRI (OR = 0.94, 95% CI = 0.85 to 1.04). Facility academic affiliation and for-profit status were inversely associated with supplemental ultrasound (OR = 0.53, 95% CI = 0.49 to 0.57, and OR = 0.83, 95% CI = 0.81 to 0.86, respectively) and positively associated with supplemental MRI (OR = 3.04, 95% CI = 2.86 to 3.46, and OR = 1.88, 95% CI = 1.66 to 2.12, respectively). Supplemental screening was more likely to occur after passage of state-specific density notification laws than before passage (OR = 3.56, 95% CI = 3.30 to 3.84, and OR = 1.79, 95% CI = 1.60 to 2.00, respectively). These results show that supplemental breast imaging utilization has been uncommon and was related to facility factors and density legislation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Beyond the AJR: Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts-Performance Affected by Facility Factors and Density Reporting Laws.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2025 Sep;225(3):e2532702. doi: 10.2214/AJR.25.32702. Epub 2025 Feb 5. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2025. PMID: 39907476 No abstract available.
References
-
- Weinstein SP, Slanetz PJ, Lewin AA, et al. ; Expert Panel on Breast Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria(R) supplemental breast cancer screening based on breast density. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021;18:S456-S473. - PubMed
-
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al. ; American Cancer Society Breast Cancer Advisory Group. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:75-89. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 CA253911/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA154292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54GM115516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA248068/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103644/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA154292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA014520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA248068/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium
- P30 CA023108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA253911/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

