Onvansertib in Combination With Chemotherapy and Bevacizumab in Second-Line Treatment of KRAS-Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Single-Arm, Phase II Trial
- PMID: 39475591
- PMCID: PMC11856007
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-24-01266
Onvansertib in Combination With Chemotherapy and Bevacizumab in Second-Line Treatment of KRAS-Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Single-Arm, Phase II Trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Onvansertib in Combination With Chemotherapy and Bevacizumab in Second-Line Treatment of KRAS-Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Single-Arm, Phase II Trial.J Clin Oncol. 2025 Jan;43(1):113. doi: 10.1200/JCO-24-02458. Epub 2024 Nov 19. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39561313 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: This phase II study evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of onvansertib, a polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibitor, in combination with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) + bevacizumab for the second-line treatment of KRAS-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC).
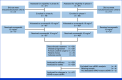
Patients and methods: This multicenter, open-label, single-arm study enrolled patients with KRAS-mutated mCRC previously treated with oxaliplatin and fluorouracil with or without bevacizumab. Patients received onvansertib (15 mg/m2 once daily on days 1-5 and 15-19 of a 28-day cycle) and FOLFIRI + bevacizumab (days 1 and 15). The primary end point was the objective response rate (ORR), and secondary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS), duration of response (DOR), and tolerability. Translational and preclinical studies were conducted in KRAS-mutant CRC.
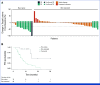
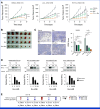
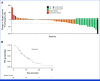
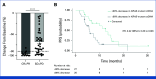
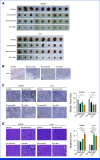
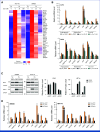
Results: Among the 53 patients treated, the confirmed ORR was 26.4% (95% CI, 15.3 to 40.3). The median DOR was 11.7 months (95% CI, 9.4 to not reached). Grade 3/4 adverse events were reported in 62% of patients. A post hoc analysis revealed that patients with no prior bevacizumab treatment had a significantly higher ORR and longer PFS compared with patients with prior bevacizumab treatment: ORR of 76.9% versus 10.0% (odds ratio of 30.0, P < .001) and median PFS of 14.9 months versus 6.6 months (hazard ratio of 0.16, P < .001). Our translational findings support that prior bevacizumab exposure contributes to onvansertib resistance. Preclinically, we showed that onvansertib inhibited the hypoxia pathway and exhibited robust antitumor activity in combination with bevacizumab through the inhibition of angiogenesis.
Conclusion: Onvansertib in combination with FOLFIRI + bevacizumab showed significant activity in the second-line treatment of patients with KRAS-mutant mCRC, particularly in patients with no prior bevacizumab treatment. These findings led to the evaluation of the combination in the first-line setting (ClinicalTrails.gov identifier: NCT06106308).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03829410 NCT06106308 NCT03829410.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et al. : Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2335-2342, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, et al. : Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFOX4) for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: Results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology group study E3200. J Clin Oncol 25:1539-1544, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bennouna J, Sastre J, Arnold D, et al. : Continuation of bevacizumab after first progression in metastatic colorectal cancer (ML18147): A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:29-37, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Tabernero J, Lakomy R, et al. : Addition of aflibercept to fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan improves survival in a phase III randomized trial in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer previously treated with an oxaliplatin-based regimen. J Clin Oncol 30:3499-3506, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Tabernero J, Yoshino T, Cohn AL, et al. : Ramucirumab versus placebo in combination with second-line FOLFIRI in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma that progressed during or after first-line therapy with bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, and a fluoropyrimidine (RAISE): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 16:499-508, 2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

