EB-SUN, a new microtubule plus-end tracking protein in Drosophila
- PMID: 39475714
- PMCID: PMC11656466
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E24-09-0402
EB-SUN, a new microtubule plus-end tracking protein in Drosophila
Abstract
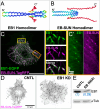
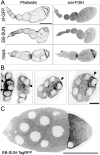
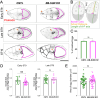
Microtubule (MT) regulation is essential for oocyte development. In Drosophila, MT stability, polarity, abundance, and orientation undergo dynamic changes across developmental stages. In our effort to identify novel microtubule-associated proteins that regulate MTs in the Drosophila ovary, we identified a previously uncharacterized gene, CG18190, which encodes a novel MT end-binding (EB) protein, which we propose to name EB-SUN. We show that EB-SUN colocalizes with EB1 at growing MT plus-ends in Drosophila S2 cells. Tissue-specific and developmental expression profiles from Paralog Explorer reveal that EB-SUN is predominantly expressed in the ovary and early embryos, while EB1 is ubiquitously expressed. Furthermore, as early as oocyte determination, EB-SUN comets are highly concentrated in oocytes during oogenesis. EB-SUN knockout (KO) results in decreased MT density at the onset of mid-oogenesis (stage 7) and delays oocyte growth during late mid-oogenesis (stage 9). Combining EB-SUN KO with EB1 knockdown (KD) in germ cells significantly further reduces MT density at stage 7. Hatching assays of single protein depletion reveal distinct roles for EB-SUN and EB1 in early embryogenesis, likely due to differences in their expression and binding partners. Notably, all eggs from EB-SUN KO/EB1 KD females fail to hatch, suggesting partial redundancy between these proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no financial conflict of interest.
Figures




Update of
-
EB-SUN, a New Microtubule Plus-End Tracking Protein in Drosophila.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 11:2024.09.11.612465. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.11.612465. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Dec 1;35(12):ar147. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-09-0402. PMID: 39314338 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO (2008). Tracking the ends: A dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9, 309–322. - PubMed
-
- Baas PW, Qiang L (2005). Neuronal microtubules: When the MAP is the roadblock. Trends Cell Biol 15, 183–187. - PubMed
-
- Bastock R, St Johnston D (2008). Drosophila oogenesis. Curr Biol 18, R1082–R1087. - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N (1993). Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118, 401–415. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

