Characterising HIV-Indicator conditions among two nationwide long-term cohorts of people living with HIV in Germany (1999-2023)
- PMID: 39476279
- PMCID: PMC12137405
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-024-02419-2
Characterising HIV-Indicator conditions among two nationwide long-term cohorts of people living with HIV in Germany (1999-2023)
Abstract
Background/objective: Information about occurrence and affected groups of symptoms/diagnoses indicative of an HIV infection (so-called HIV indicator conditions; HIV-ICs) is lacking. We analyse HIV-IC incidence, transmission risks and immune status among people living with HIV (PLWH) antiretroviral therapy (ART) naive.
Methods: Diagnoses reported for ART-naive PLWH from two multicentre observational, prospective cohort studies between 1999-2023 were analysed. Incidence rates per 1,000 person-years (PYs) were calculated for the overall study period and time periods defined by ART treatment recommendations. For further description, CD4 counts around HIV-IC diagnosis (+ -30 days) and HIV-transmission routes were collected.
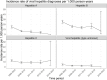
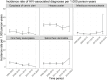
Results: In total 15,940 diagnoses of 18,534 PLWH in Germany were included. Of those 81% were male (median age: 36 years) and 56% reported being men, who have sex with men as the likely HIV-transmission route. Incidence rates varied between the different HIV-ICs. Syphilis had the highest incidence rate (34 per 1,000 PYs; 95% confidence interval [CI] 29-40) for sexually transmitted infections (STIs), hepatitis B was highest for viral hepatitis diagnoses (18 per 1,000 PYs; 95% CI 17-20); according to CDC-classification herpes zoster for HIV-associated diagnoses (22 per 1,000; 95% CI 20-24) and candidiasis for AIDS-defining diagnoses (30 per 1,000 PYs; 95% CI 29-32). Most PLWH with HIV-ICs (hepatitis, HIV-associated diagnoses and AIDS-defining conditions) had CD4 cell counts < 350.
Conclusion: This analysis characterizes HIV-ICs regarding the incidence, HIV-transmission route and patients' immune status. The results underline the importance of HIV-IC-based screening to detect PLWH with already partially impaired immune status and in need of timely ART initiation.
Keywords: AIDS; Acquired immune deficiency syndrome; Cohort studies; Germany; HIV; Human immunodeficiency virus; Indicator conditions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: GB: Grants or contracts from Niedersächsisches Ministerium für Wissenschaft und Kultur, COFONI Network, and European Regional Development Fund, consulting fees Gilead, ViiV, MSD, Virology Education, Janssen, payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Gilead, ViiV, MSD, Virology Education, Janssen, support for attending meetings and/or travel from DZIF, NEAT ID Foundation, Participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board of TherVacB_Phase1a. CB: Grants or contracts from DZIF, DFG and Hector Foundation, consulting fees from Abbvie, Gilead, JnJ, MSD, and ViiV, payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Abbvie, Gilead, JnJ, MSD, and ViiV, support for attending meetings and/or travel from Abbvie, Gilead, JnJ, MSD, and ViiV. SE: Grants or contracts from Gilead, Janssen, MSD, and ViiV consulting fees from Gilead, GSK, Janssen, MSD, and ViiV, payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Gilead, Janssen, MSD, and ViiV, support for attending meetings and/or travel from Gilead, Janssen, MSD, and ViiV, Leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group, paid or unpaid in DAIG, DAGNÄ, DSTIG, DDG, DGI, Regional commission AIDS NRW. UK: Support for attending meetings and/or travel from ECDC, German AIDS Society, German STI Society, and European AIDS Society; UK owns ‘Exchange-traded fund’ (ETF) shares, which includes stocks of companies that are involved in health care. The remaining authors have no competing interests to declare. Ethical approval: The HIV-1 Seroconverter Study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Charité University Medicine Berlin (EA2/024/21). Participants of the HIV-1 Seroconverter Study provide their written informed consent to participate. The ClinSurv-HIV Study data (1999–2018) were collected anonymously and in compliance with the German Infection Protection Act (IfSG, 2001). Consent to participate: These data did therefore not require written informed consent. Approval for this was granted by the RKI data protection officer and the Federal Commissioner for Data Protection and Freedom of Information.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Global health sector strategies on, respectively, HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections for the period 2022–2030. 2022. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/360348/9789240053779-eng.pdf.... Accessed 14 Jun 2024.
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. Fast-Track: ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030. 2014. https://www.aidsdatahub.org/sites/default/files/resource/unaids-fast-tra.... Accessed 14 Jun 2024.
-
- Eisinger RW, Dieffenbach CW, Fauci AS. HIV viral load and transmissibility of HIV infection: Undetectable equals untransmittable. JAMA. 2019;321:451–2. 10.1001/jama.2018.21167. - PubMed
-
- der Heiden M, an, Marcus U, Kollan C, Schmidt D, Koppe U, Gunsenheimer-Bartmeyer B, Bremer V. Schätzung der Anzahl der HIV-Neuinfektionen in den Jahren. und 2023 sowie der Gesamtzahl der Menschen, die Ende 2023 mit HIV in Deutschland leben. Epidemiologisches Bulletin. 2022;2024:3–20. 10.25646/12212.
-
- Lauscher P, Hanhoff N, Valbert F, Schewe K, Koegl C, Bickel M, et al. Socio-demographic and psycho-social determinants of HIV late presentation in Germany - results from the FindHIV study. AIDS Care. 2023;35:1749–59. 10.1080/09540121.2023.2185196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

