Copper Drives Remodeling of Metabolic State and Progression of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 39476412
- PMCID: PMC11803400
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0187
Copper Drives Remodeling of Metabolic State and Progression of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
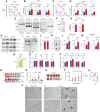
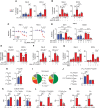
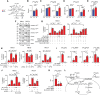
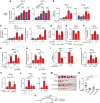
The work establishes a requirement for glucose-dependent coordination between energy production and redox homeostasis, which is fundamental for the survival of cancer cells that accumulate Cu and contributes to tumor growth.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
B. Vemuri, J.A. Landero Figueroa, J.Meller, J.T. Cunningham, M.F. Czyzyk-Krzeska report a patent for US Patent App.17/327,100, 2022 pending. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures

Update of
-
Copper drives remodeling of metabolic state and progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 19:2024.01.16.575895. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.16.575895. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cancer Discov. 2025 Feb 07;15(2):401-426. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0187. PMID: 38293110 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Wood E, Donin N, Shuch B. Adjuvant therapy for localized high-risk renal cell carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am 2020;47:345–58. - PubMed
-
- Choueiri TK, Tomczak P, Park SH, Venugopal B, Ferguson T, Chang Y-H, et al. Adjuvant pembrolizumab after nephrectomy in renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2021;385:683–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA259845/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA259845/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 GM128216/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA287260/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- T32ES007250/NIH ESI
- R35 GM146878/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA236764/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08CA273542/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA287260/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA196516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA196516/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- T32CA17846/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R37 CA272854/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35GM146878/National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 CA230904/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001110/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30CA046934/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- K08 CA273542/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007250/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA239657/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37CA272854/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R35 GM133561/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2I01BX001110/Veteran Administration
- R01CA239657/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R35GM133561/National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01GM128216/National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01CA230904/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- T32CA236764/National Cancer Institute (NCI)

