Brief guide to RT-qPCR
- PMID: 39476972
- PMCID: PMC11612376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100141
Brief guide to RT-qPCR
Abstract
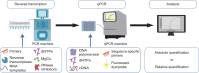
RNA quantification is crucial for understanding gene expression and regulation. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) is a widely used technique for RNA quantification because of its practical and quantitative nature, sensitivity, and specificity. Here, we provide an overview of RT-qPCR, focusing on essential reagents, the importance of primer design, the detailed workflow, and data analysis methods. This guide will be useful for scientists who are unfamiliar with RT-qPCR, highlighting key considerations for successful RNA quantification.
Keywords: RNA quantification; Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interests The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Adams G. A beginner’s guide to RT-PCR, qPCR and RT-qPCR. Biochemist. 2020;42(3):48–53.
-
- Arabkari V., Clancy E., Dwyer R.M., Kerin M.J., Kalinina O., Holian E., Smith T.J. Relative and absolute expression analysis of microRNAs associated with luminal a breast cancer–a comparison. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020;26:833–844. - PubMed
-
- Bachman J. Reverse-transcription PCR (rt-PCR) Methods Enzymol. 2013;530:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Bustin S.A., Benes V., Nolan T., Pfaffl M.W. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR–a perspective. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005;34(3):597–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

