Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates for patients with HR+/HER2- high-risk, early-stage breast cancer (EBC) by clinical and molecular features in the phase II I-SPY2 clinical trial
- PMID: 39477071
- PMCID: PMC12252650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.10.018
Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates for patients with HR+/HER2- high-risk, early-stage breast cancer (EBC) by clinical and molecular features in the phase II I-SPY2 clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative early-stage breast cancer (EBC) is a heterogenous disease. Identification of better clinical and molecular biomarkers is essential to guide optimal therapy for each patient.
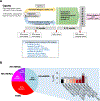
Patients and methods: We analyzed rates of pathologic complete response (pCR) and distant recurrence-free survival (DRFS) for patients with HR+/HER2-negative EBC in eight neoadjuvant arms in the I-SPY2 trial by clinical/molecular features: age, stage, histology, percentage estrogen receptor (ER) positivity, ER/progesterone receptor status, MammaPrint (MP)-High1 (0 to -0.57) versus MP-High2 (<-0.57), BluePrint (BP)-Luminal-type versus BP-Basal-type, and ImPrint immune signature. We quantified the clinical/molecular heterogeneity, assessed overlap among these biomarkers, and evaluated associations with pCR and DRFS.
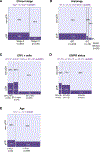
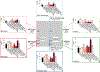
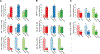
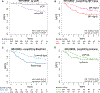
Results: Three hundred and seventy-nine patients with HR+/HER2-negative EBC were included in this analysis, with an observed pCR rate of 17% across treatment arms. pCR rates were higher in patients with stage II versus III disease (21% versus 9%, P = 0.0013), ductal versus lobular histology (19% versus 11%, P = 0.049), lower %ER positivity (≤66% versus >66%) (35% versus 9%, P = 3.4E-09), MP-High2 versus MP-High1 disease (31% versus 11%, P = 1.1E-05), BP-Basal-type versus BP-Luminal-type disease (34% versus 10%, P = 1.62E-07), and ImPrint-positive versus -negative disease (38% versus 10%, P = 1.64E-09). Patients with lower %ER were more likely to have MP-High2 and BP-Basal-type disease. At a median follow-up of 4.8 years, patients who achieved pCR had excellent outcomes irrespective of clinical/molecular features. Among patients who did not achieve pCR, DRFS events were more frequent in patients with MP-High2 and BP-Basal-type disease than those with MP-High1 and BP-Luminal-type disease.
Conclusions: Among patients with high molecular-risk HR+/HER2-negative EBC, the MP-High2, BP-Basal-type, and ImPrint-positive signatures identified a partially overlapping subset of patients who were more likely to achieve pCR in response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy ± targeted agents or immunotherapy compared to patients with MP-High1, BP-Luminal-type, and ImPrint-negative disease. I-SPY2.2 is incorporating the use of these biomarkers to molecularly define specific patient populations and optimize treatment selection.
Keywords: MammaPrint; basal; intrinsic subtype; luminal; molecular subtype; neoadjuvant therapy.
Copyright © 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune Subtyping Identifies Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer Who Respond to Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy (IO): Results From Five IO Arms of the I-SPY2 Trial.JCO Precis Oncol. 2025 Jun;9:e2400776. doi: 10.1200/PO-24-00776. Epub 2025 Jun 17. JCO Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40526879 Free PMC article.
-
Combined prognostic impact of initial clinical stage and residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant systemic therapy in triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer: an analysis of the I-SPY2 randomized clinical trial.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 23;27(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-02070-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40551254 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tumor Intrinsic Subtypes and Gene Expression Signatures in Early-Stage ERBB2/HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of CALGB 40601, NeoALTTO, and NSABP B-41 Trials.JAMA Oncol. 2024 May 1;10(5):603-611. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.7304. JAMA Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38546612 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Current Literature and Real-World Outcomes With Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2 Negative Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2025 Jul;25(5):e666-e677. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2025.03.008. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Clin Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40180865 Review.
Cited by
-
De-escalated neoadjuvant nab-paclitaxel combined with pyrotinib and trastuzumab in intrinsic HER2-enriched breast cancer (NJMU-BC01): a multicenter, single-arm, phase 2 trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Jul 19;86:103376. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103376. eCollection 2025 Aug. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40727010 Free PMC article.
-
Selective elimination of surgery for early invasive breast cancer: promise, challenges, and prospects.Gland Surg. 2025 Jul 31;14(7):1187-1190. doi: 10.21037/gs-2025-191. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Gland Surg. 2025. PMID: 40771391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Gene Expression Signatures for Guiding Initial Therapy in ER+/HER2- Early Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 28;17(9):1482. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091482. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Subtyping Identifies Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer Who Respond to Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy (IO): Results From Five IO Arms of the I-SPY2 Trial.JCO Precis Oncol. 2025 Jun;9:e2400776. doi: 10.1200/PO-24-00776. Epub 2025 Jun 17. JCO Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40526879 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and molecular features of HR + /HER2 - breast cancer patients with distinct endocrine resistance patterns.Chin J Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 30;37(1):48-65. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2025.01.04. Chin J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40078562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cejalvo JM, Pascual T, Fernández-Martínez A, et al. Clinical implications of the non-luminal intrinsic subtypes in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;67:63–70. - PubMed
-
- NCCN. NCCN Guidelines: Breast Cancer. Published online April 2022. Available at: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/recently-published-guidelines. Accessed July 15, 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

