Atractylenolide I inhibits angiogenesis and reverses sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma through ATP6V0D2-mediated autophagic degradation of EPAS1/HIF2α
- PMID: 39477683
- PMCID: PMC11849937
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2421699
Atractylenolide I inhibits angiogenesis and reverses sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma through ATP6V0D2-mediated autophagic degradation of EPAS1/HIF2α
Abstract
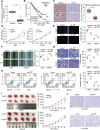
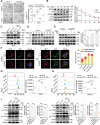
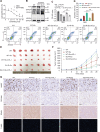
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is tightly associated with VHL (von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor) mutation and dysregulated angiogenesis. Accumulating evidence indicates that antiangiogenic treatment abolishing tumor angiogenesis can achieve longer disease-free survival in patients with ccRCC. Atractylenolide I (ATL-I) is one of the main active compounds in Atractylodes macrocephala root extract and exhibits various pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory and antitumor effects. In this study, we revealed the potent antitumor activity of ATL-I in ccRCC. ATL-I exhibited robust antiangiogenic capacity by inhibiting EPAS1/HIF2α-mediated VEGFA production in VHL-deficient ccRCC, and it promoted autophagic degradation of EPAS1 by upregulating the ATPase subunit ATP6V0D2 (ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit d2) to increase lysosomal function and facilitated fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes. Mechanistically, ATP6V0D2 directly bound to RAB7 and VPS41 and promoted the RAB7-HOPS interaction, facilitating SNARE complex assembly and autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Moreover, ATP6V0D2 promoted autolysosome degradation by increasing the acidification and activity of lysosomes during the later stages of macroautophagy/autophagy. Additionally, we found that ATL-I could decrease the level of EPAS1, which was upregulated in sunitinib-resistant cells, thus reversing sunitinib resistance. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that ATL-I is a robust antiangiogenic and antitumor lead compound with potential clinical application for ccRCC therapy.Abbreviations: ATL-I: atractylenolide I; ATP6V0D2: ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit d2; CAM: chick chorioallantoic membrane; ccRCC: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; CTSB: cathepsin B; CTSD: cathepsin D; GO: Gene Ontology; HIF-1: HIF1A-ARNT heterodimer; HOPS: homotypic fusion and protein sorting; KDR/VEGFR: kinase insert domain receptor; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; RCC: renal cell carcinoma; SNARE: soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; TEM: transmission electron microscopy; TKI: tyrosine kinase inhibitor; V-ATPase: vacuolar-type H±translocating ATPase; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; VHL: von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor.
Keywords: ATP6V0D2; Atractylenolide I; HIF2α; autophagic degradation; clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
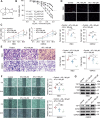
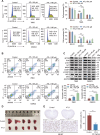
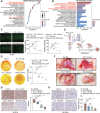
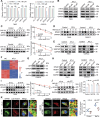

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
