Towards integrated malaria molecular surveillance in Africa
- PMID: 39477780
- PMCID: PMC11984316
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2024.09.005
Towards integrated malaria molecular surveillance in Africa
Abstract
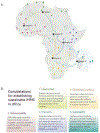
Integrated malaria molecular surveillance (iMMS) systems are essential for Africa's expanding malaria genomics initiatives. Here we highlight a few initiatives and demonstrate how iMMS can support evidence-based decisions and policies for National Malaria Programs and other malaria control stakeholders. We conclude with key considerations for advancing these malaria genomics initiatives towards sustainable iMMS.
Keywords: genomic surveillance; genomics; malaria; molecular surveillance; regional hubs.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Global genomic surveillance strategy for pathogens with pandemic and epidemic potential, 2022–2032[Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240046979. [Accessed: 19-Jan-2024] - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

