Treatment of COVID-19 Associated Olfactory Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39477832
- PMCID: PMC11525399
- DOI: 10.1007/s11882-024-01182-6
Treatment of COVID-19 Associated Olfactory Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Purpose of review: COVID -19 associated olfactory dysfunction is widespread, yet effective treatment strategies remain unclear. This article aims to provide a comprehensive systematic review of therapeutic approaches and offers evidence-based recommendations for their clinical application.
Recent findings: A living Cochrane review, with rigorous inclusion criteria, has so far included 2 studies with a low certainty of evidence. In this systematic review we list clinical data of 36 randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomised studies published between Jan 1, 2020 and Nov 19, 2023 regarding treatment options for COVID-19 associated olfactory dysfunction. Nine treatment groups were analysed, including olfactory training, local and systemic corticosteroids, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), calcium chelators, vitamin supplements including palmitoylethanolamide with luteolin, insulin, gabapentin and cerebrolysin. Primary objective was the effect of the studied treatments on the delta olfactory function score (OFS) for objective/psychophysical testing. Treatments such as PRP and calcium chelators demonstrated significant improvements on OFS, whereas olfactory training and corticosteroids did not show notable efficacy for COVID-19 associated olfactory dysfunction.
Keywords: COVID-19; Olfactory dysfunction; Treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
HippoDx (stocks and scientific advisory board), speakers fees from GSK.
Figures
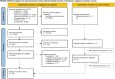
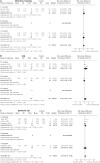

References
-
- Borsetto D, Hopkins C, Philips V, Obholzer R, Tirelli G, Polesel J, et al. Self-reported alteration of sense of smell or taste in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis on 3563 patients. Rhinology. 2020;58(5):430–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

