Perceptions of building-integrated nature-based solutions by suppliers versus consumers in Egypt
- PMID: 39477967
- PMCID: PMC11525813
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-76014-8
Perceptions of building-integrated nature-based solutions by suppliers versus consumers in Egypt
Abstract
Can Building-Integrated Nature-based Solutions (BI-NbS) reach their full potential in the Global South? In the Egyptian context, BI-NbS are relatively new with an identified gap between the high potential in theory and low implementation rates in practice. To bridge this gap, the study conducts an in-depth investigation of BI-NbS market conditions to reveal the current trends in the residential buildings market in Egypt. It also identifies the gaps and overlaps in the perceptions of the suppliers and consumers of BI-NbS. Results reveal that the residential sector sales mainly target high-income groups yet very limited and dominated by rooftop systems. Suppliers advocate for high-tech systems over low-tech systems, whereas consumers prefer the latter. The perceptions of suppliers and consumers mostly align regarding the basic aspects such as the production and operation preferences as well as the anxieties and concerns about the relatively new BI-NbS in this regional context. However, they diverge in key aspects affecting market penetration such as implementation conditions, aims, and barriers. Accordingly, the study identified the gap between suppliers and consumers, and outlined recommendations, directed to suppliers and policymakers, for improved market development and local implementation of BI-NbS in emerging markets of the Global South, such as Egypt.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial and/or non-financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures



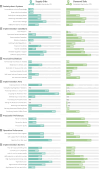

References
-
- Eggermont, H. et al. Nature-based solutions: New influence for environmental management and research in Europe. GAIA - Ecol. Perspect. Sci. Soc. 24, 243–248 (2015).
-
- Cohen-Shacham, E., Walters, G., Janzen, C. & Maginnis, S. Nature-Based Solutions to Address Global Societal Challenges (IUCN, 2016). 10.2305/iucn.ch.2016.13.en.
-
- Wójcik-Madej, J. & Sowińska-Świerkosz, B. Pre-existing interventions as nbs candidates to address societal challenges. Sustain 14, (2022).
-
- Goodwin, S., Olazabal, M., Castro, A. J. & Pascual, U. Global mapping of urban nature-based solutions for climate change adaptation. Nat. Sustain. 6, 458–469 (2023). - DOI
-
- Lakshmisha, A., Nazar, A. F. & Nagendra, H. Nature based solutions in cities of the global South—The ‘where, who and how’ of implementation. Environ. Res. Ecol. 3, 025005 (2024). - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

