Structural basis for human OGG1 processing 8-oxodGuo within nucleosome core particles
- PMID: 39477986
- PMCID: PMC11526172
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53811-3
Structural basis for human OGG1 processing 8-oxodGuo within nucleosome core particles
Abstract
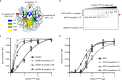
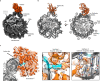
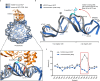
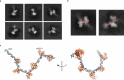
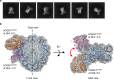
Base excision repair (BER) is initialized by DNA glycosylases, which recognize and flip damaged bases out of the DNA duplex into the enzymes active site, followed by cleavage of the glycosidic bond. Recent studies have revealed that all types of DNA glycosylases repair base lesions less efficiently within nucleosomes, and their repair activity is highly depended on the lesion's location within the nucleosome. To reveal the underlying molecular mechanism of this phenomenon, we determine the 3.1 Å cryo-EM structure of human 8-oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase 1 (hOGG1) bound to a nucleosome core particle (NCP) containing a common oxidative base lesion, 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodGuo). Our structural analysis shows that hOGG1 can recognize and flip 8-oxodGuo even within NCPs; however, the interaction between 8-oxodGuo and hOGG1 in a NCP context is weaker than in free DNA due to competition for nucleosomal DNA by the histones. Binding of OGG1 and the flipping of 8-oxodGuo by hOGG1 leads to a partial detachment of DNA from the histone core and a ratchet-like inward movement of nucleosomal DNA. Our findings provide insights into how the dynamic structure of nucleosomes modulate the activity of repair enzymes within chromatin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 22377059/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- SFB1361-project ID 393547839/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- TRR237-project ID 369799452/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- HO2489/11-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

