A multi-modal single-cell and spatial expression map of metastatic breast cancer biopsies across clinicopathological features
- PMID: 39478111
- PMCID: PMC11564109
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03215-z
A multi-modal single-cell and spatial expression map of metastatic breast cancer biopsies across clinicopathological features
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: A multi-modal single-cell and spatial expression map of metastatic breast cancer biopsies across clinicopathological features.Nat Med. 2025 May;31(5):1713. doi: 10.1038/s41591-025-03665-z. Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 40155562 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
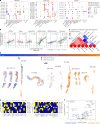
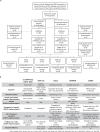
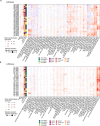
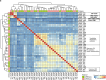
Although metastatic disease is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths, its tumor microenvironment remains poorly characterized due to technical and biospecimen limitations. In this study, we assembled a multi-modal spatial and cellular map of 67 tumor biopsies from 60 patients with metastatic breast cancer across diverse clinicopathological features and nine anatomic sites with detailed clinical annotations. We combined single-cell or single-nucleus RNA sequencing for all biopsies with a panel of four spatial expression assays (Slide-seq, MERFISH, ExSeq and CODEX) and H&E staining of consecutive serial sections from up to 15 of these biopsies. We leveraged the coupled measurements to provide reference points for the utility and integration of different experimental techniques and used them to assess variability in cell type composition and expression as well as emerging spatial expression characteristics across clinicopathological and methodological diversity. Finally, we assessed spatial expression and co-localization features of macrophage populations, characterized three distinct spatial phenotypes of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and identified expression programs associated with local T cell infiltration versus exclusion, showcasing the potential of clinically relevant discovery in such maps.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
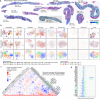
Figures











References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 1P50CA168504/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 2019_A70/Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung (Else Kroner-Fresenius Foundation)
- P50 CA168504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201500003C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261100039 / HHSN26120150000/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- LT000452/2019-L/Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP)
- HHSN261201500003I/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ALTF 738-2017/European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO)
- 17095/Conquer Cancer Foundation (Conquer Cancer Foundation of the American Society of Clinical Oncology)
- T32 CA009172/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

