Serum anti-NMDA receptor antibodies are linked to memory impairment 12 months after stroke
- PMID: 39478168
- PMCID: PMC11919755
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-024-02744-w
Serum anti-NMDA receptor antibodies are linked to memory impairment 12 months after stroke
Abstract
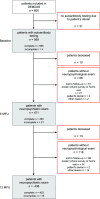
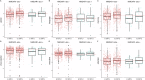
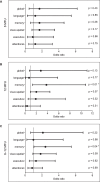
Patients suffering from strokes are at increased risk of developing post-stroke dementia. Serum anti-NMDA receptor autoantibodies (NMDAR1-abs) have been associated with unfavorable post-stroke outcomes. However, their effect on specific cognitive domains remains unclear. We used data from the prospective multicenter DZNE-mechanisms after stroke (DEMDAS) cohort, and measured NMDAR1-abs in serum at baseline. Cognitive function was assessed with a comprehensive neuropsychological test battery at 6- and 12-months follow-up. We employed crude and stepwise confounder adjusted linear and logistic regression models as well as generalized estimating equation models (GEE) to determine the relevance of NMDAR1-abs seropositivity on cognitive function after stroke. 10.2% (58/569) DEMDAS patients were NMDAR1-abs seropositive (IgM:n = 44/IgA:n = 21/IgG:n = 2). Seropositivity was not associated with global cognitive impairment after stroke. However, NMDAR1-abs seropositive patients performed lower in the memory domain (βadjusted = -0.11; 95%CI = -0.57 to -0.03) and were at increased risk for memory impairment (ORadjusted = 3.8; 95%CI = 1.33-10.82) compared to seronegative patients, 12 months after stroke. Further, NMDAR1-abs were linked to memory impairment over time in GEE from 6- to 12-months follow-up (ORadjusted = 2.41; 95%CI = 1.05-5.49). Our data suggests that NMDAR1-abs contribute to memory dysfunction 1 year after stroke while not affecting other cognitive subdomains. Hence, antineuronal autoimmunity may be involved in distinct mechanisms of post-stroke memory impairment. Clinical trial name and registration number: The Determinants of Dementia After Stroke (DEMDAS; study identifier on clinical trials.gov: NCT01334749).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: ME reports grants from Bayer and fees paid to the Charité from Abbot, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Sanofi, Novartis, Pfizer, all outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM. Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:1006–18. - PubMed
-
- Dichgans M, Zietemann V. Prevention of vascular cognitive impairment. Stroke. 2012;43:3137–46. - PubMed
-
- Dahm L, Ott C, Steiner J, Stepniak B, Teegen B, Saschenbrecker S, et al. Seroprevalence of autoantibodies against brain antigens in health and disease. Ann Neurol. 2014;76:82–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

