RAS-mutant leukaemia stem cells drive clinical resistance to venetoclax
- PMID: 39478230
- PMCID: PMC11618090
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08137-x
RAS-mutant leukaemia stem cells drive clinical resistance to venetoclax
Abstract
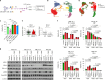
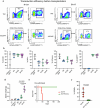
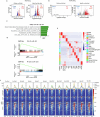
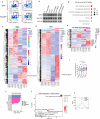
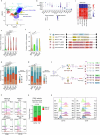
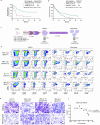
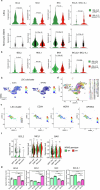
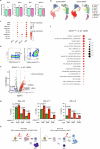
Cancer driver mutations often show distinct temporal acquisition patterns, but the biological basis for this, if any, remains unknown. RAS mutations occur invariably late in the course of acute myeloid leukaemia, upon progression or relapsed/refractory disease1-6. Here, by using human leukaemogenesis models, we first show that RAS mutations are obligatory late events that need to succeed earlier cooperating mutations. We provide the mechanistic explanation for this in a requirement for mutant RAS to specifically transform committed progenitors of the myelomonocytic lineage (granulocyte-monocyte progenitors) harbouring previously acquired driver mutations, showing that advanced leukaemic clones can originate from a different cell type in the haematopoietic hierarchy than ancestral clones. Furthermore, we demonstrate that RAS-mutant leukaemia stem cells (LSCs) give rise to monocytic disease, as observed frequently in patients with poor responses to treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax. We show that this is because RAS-mutant LSCs, in contrast to RAS-wild-type LSCs, have altered BCL2 family gene expression and are resistant to venetoclax, driving clinical resistance and relapse with monocytic features. Our findings demonstrate that a specific genetic driver shapes the non-genetic cellular hierarchy of acute myeloid leukaemia by imposing a specific LSC target cell restriction and critically affects therapeutic outcomes in patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.K. receives research support from Klondike, AbbVie and Janssen, and consulting fees from AbbVie, Syndax, Novartis, Servier, AbbVie, Menarini-Stemline Therapeutics, Adaptive, Dark Blue Therapeutics, MEI Pharma, Legend Biotech, Sanofi Aventis, Auxenion GmbH, Vincerx, Curis, Intellisphere and Janssen. D.A.L. is an advisory board member of Mission Bio, Veracyte, Pangea and Alethiomics and has received research support from Ultima Genomics unrelated to this work. A.M. receives research support from Chimeric Therapeutics, Lin Biosciences, Hibercell Inc., Qurient and Molecular Templates, Inc. C.D.D. has received consulting fees from Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Astellas, GenMab, Notable Labs, Rigel and Servier. E.P. is cofounder of, and holds a fiduciary role in Isabl Inc. P.L. has received grants to his Institution from Amgen, Mirati, Revolution Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim and Virtec Pharmaceuticals. P.L. is an advisory board member of Frontier Medicines, Ikena, Biotheryx and PAQ-Tx (consulting fees and equity in each) and has received consulting fees or honoraria from Black Diamond Therapeutics, AmMax, OrbiMed, PAQ-Tx, Repare Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim and Revolution Medicines. EPP has received consulting fees or honoraria from Janssen, Daiichi Sankyo and Cellarity, unrelated to the current study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R33 CA267219/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA235622/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA273232/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA283574/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA260711/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL157387/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA271418/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR004419/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA196521/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA254130/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA279264/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA129243/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA271331/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

