The Combination of Curcumae Radix and Syzygium Aromaticum Extracts Mitigates Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia through Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- PMID: 39478652
- PMCID: PMC12257320
- DOI: 10.5534/wjmh.240071
The Combination of Curcumae Radix and Syzygium Aromaticum Extracts Mitigates Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia through Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Abstract
Purpose: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a urinary tract disorder that primarily affects geriatric males. Natural materials have been developed to treat and prevent symptoms of BPH. However, a few natural functional foods has been conclusively proven to cure or prevent symptoms of BPH. The study aimed to investigate the anti-proliferative mechanism of Curcumae Radix (CR) and Syzygium aromaticum (SA) extracts using RWPE-1 cells and testosterone propionate (TP)-induced BPH rats.
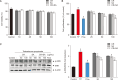
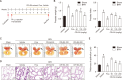
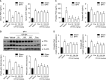
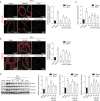
Materials and methods: In vitro experiments were performed to assess the synergistic anti-proliferative effects of an equal mixture of CR and SA extracts on TP-treated RWPE-1 cells. In animal experiments, TP-induced BPH rats were administrated with saline, CR and SA extracts at 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg or finasteride at 1 mg/kg daily for 6 weeks. Body weight, prostate weight, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), androgen receptor (AR), and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels were measured. Additionally, extracellular signal-regulated kinase and NF-κB levels, oxidative stress, and inflammatory stress responses in the prostate were also analyzed.
Results: In this study, the combination of CR and SA extracts synergistically inhibited cell proliferation compared with the effect of each extract in TP-treated RWPE-1 cells. CR and SA extracts inhibited increasing of prostate weight, thickness of prostate epithelium, the level of PSA and DHT in serum. The expression of protein and gene of PSA and AR in prostate of TP-induced BPH rats were also suppressed by the administration of CR and SA extracts. Furthermore, reactive oxygen species and inflammation axis, NOX4-iNOS-COX2 and its associated representative inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-8 were also reduced in the CR and SA extracts-administered BPH rats.
Conclusions: The results suggest that the combination of CR and SA extracts improves BPH through its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects, demonstrating great potential as an anti-BPH medicine.
Keywords: Androgen receptors; Curcuma; Prostate-specific antigen; Prostatic hyperplasia; Syzygium aromaticum; Testosterone propionate.
Copyright © 2025 Korean Society for Sexual Medicine and Andrology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- De Nunzio C, Aronson W, Freedland SJ, Giovannucci E, Parsons JK. The correlation between metabolic syndrome and prostatic diseases. Eur Urol. 2012;61:560–570. - PubMed
-
- Tsunemori H, Sugimoto M. Effects of inflammatory prostatitis on the development and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a literature review. Int J Urol. 2021;28:1086–1092. - PubMed
-
- Wilson JD. Recent studies on the mechanism of action of testosterone. N Engl J Med. 1972;287:1284–1291. - PubMed
-
- Harman SM, Metter EJ, Tobin JD, Pearson J, Blackman MR Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Longitudinal effects of aging on serum total and free testosterone levels in healthy men. Baltimore longitudinal study of aging. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:724–731. - PubMed
-
- Gray A, Feldman HA, McKinlay JB, Longcope C. Age, disease, and changing sex hormone levels in middle-aged men: results of the Massachusetts male aging study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991;73:1016–1025. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

