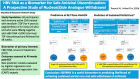
Hepatitis B Virus RNA as a Biomarker for Safe Antiviral Discontinuation: A Prospective Study of Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Withdrawal
- PMID: 39478672
- PMCID: PMC12128069
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiae541
Hepatitis B Virus RNA as a Biomarker for Safe Antiviral Discontinuation: A Prospective Study of Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Withdrawal
Abstract
Background: Withdrawal of nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy is associated with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) loss and sustained off-therapy partial cure (normal alanine aminotransferase [ALT] ≤30 U/L for males and ≤20 U/L for females with hepatitis B virus [HBV] DNA <2000 IU/mL) but should be offered only to those most likely to benefit. HBV RNA may be useful for risk stratification.
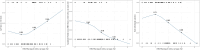
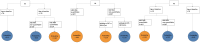
Methods: The Hepatitis B Research Network Immune-Active Trial prospectively evaluated treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) for 192 weeks ± peginterferon alfa-2a for the initial 24 weeks, followed by protocolized withdrawal of TDF among eligible participants (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01369212). HBV RNA was evaluated as a predictor of ALT flares and sustained partial cure (HBV DNA <2000 IU/mL) 48 weeks after TDF withdrawal.
Results: Of 93 participants discontinuing TDF (n = 52, TDF + peginterferon alfa-2a; n = 41, TDF alone), 52 (55.9%) had unquantifiable HBV RNA at end of treatment. ALT flares >5 times the upper limit of normal at 48 weeks off therapy occurred in 33.3%, with pretreatment age (≥35 years) and quantifiable HBV RNA at end of treatment the best predictors (area under the receiver operating characteristic curves, 0.74 and 0.85 for training and test sets, respectively). A total of 26 (28.3%) had sustained partial cure, 3 (11.5%) with ALT flare. Nonquantifiable HBV RNA and quantitative HBsAg <100 IU/mL at end of treatment were the best predictors of sustained partial cure (area under the receiver operating characteristic curves, 0.84 and 0.93 for training and test sets). If HBV RNA was quantifiable at end of treatment, the likelihood of sustained partial cure was only 3%, whereas if HBV RNA was unquantifiable and quantitative HBsAg was <100 IU/mL, this likelihood was 73%.
Conclusions: HBV RNA is a useful biomarker in predicting likelihood of achieving sustained partial cure and safe withdrawal of nucleos(t)ide analogues.
Keywords: ALT flare; HBsAg loss; functional cure; partial cure; peginterferon.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. J. J. F.: paid consulting for AbbVie and Roche. A. S. L.: paid consulting for Abbott Laboratories and Roche. G. C.: Abbott employee and shareholder. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Yip TC, Wong GL, Wong VW, et al. Durability of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in untreated and nucleos(t)ide analogue-treated patients. J Hepatol 2017; 68:63–72. - PubMed
-
- Kim GA, Lim YS, An J, et al. HBsAg seroclearance after nucleoside analogue therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B: clinical outcomes and durability. Gut 2014; 63:1325–32. - PubMed
-
- Liu F, Wang XW, Chen L, Hu P, Ren H, Hu HD. Systematic review with meta-analysis: development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016; 43:1253–61. - PubMed
-
- Chen CH, Hung CH, Wang JH, Lu SN, Hu TH, Lee CM. Long-term incidence and predictors of hepatitis B surface antigen loss after discontinuing nucleoside analogues in noncirrhotic chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin Microbiol Infect 2018; 24:997–1003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

