Qualification of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantification of anti-Vi IgG in human sera
- PMID: 39478859
- PMCID: PMC11521798
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466869
Qualification of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantification of anti-Vi IgG in human sera
Abstract
Effective vaccines against Salmonella Typhi, targeting the Vi capsular polysaccharide, have been developed and are being introduced into routine immunization in endemic countries. Vi conjugated vaccines are also being tested in new multi-component vaccine formulations. Simple, high-throughput and cost-effective assays to quantify Vi-specific IgG in clinical sera are needed. In this study we present the development and qualification of a new anti-Vi ELISA with continuous readout, which expresses results as ELISA Unit/mL (EU/mL). We have qualified the assay in terms of precision, linearity and specificity, demonstrating performance in line with a commercially available anti-Vi ELISA. We have also calibrated the assay against the 16/138 anti-Vi international standard and established conversion factor between EU/mL and international units/mL, to allow comparability of results across studies. In summary, this new assay met all the suitability criteria and is being used to evaluate anti-Vi responses in clinical studies.
Keywords: Vi; antibodies; enteric fever; enzyme - linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); human; typhoid; vaccine.
Copyright © 2024 Carducci, Massai, Lari, Semplici, Aruta, De Simone, Piu, Montomoli, Berlanda Scorza, Grappi, Iturriza-Gómara, Canals, Rondini and Rossi.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was sponsored by GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA. GSK Vaccines Institute for Global Health Srl is an affiliate of GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA. MC, LM, MS, DS, MI-G, FS, SR, RC and O.R. are employees of the GSK group of companies. FS, MI-G, RC, SR, MC, and OR report ownership of GSK shares/share options. EL, BS, PP, EM, SG are employees of Vismederi Srl. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission.
Figures

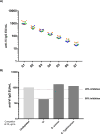

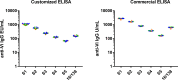
References
-
- Hancuh M, Walldorf J, Minta AA, Tevi-Benissan C, Christian KA, Nedelec Y, et al. Typhoid fever surveillance, incidence estimates, and progress toward typhoid conjugate vaccine introduction - worldwide, 2018-2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2023) 72:171–6. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7207a2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Felix A, Camb. R. M P B.A. A new antigen of b. typhosus: its relation to virulence and to active and passive immunisation. Lancet. (1934) 224:186–91. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)44360-6 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

